Model Data Using Regression and Curve Fitting
This example shows how to execute MATLAB® data regression and curve fitting in Microsoft® Excel® using a worksheet and a VBA macro.
The example organizes and displays the input and output data in a Microsoft Excel worksheet. Spreadsheet Link™ functions copy the data to the MATLAB workspace and execute MATLAB computational and graphic functions. The VBA macro also returns output data to a worksheet.
To work with VBA code in Excel with Spreadsheet Link, you must enable Spreadsheet Link as a reference in the Microsoft Visual Basic® Editor. For details, see Installation.
Open the ExliSamp.xls file and select the Sheet1 worksheet.
For help finding the ExliSamp.xls file, see Installation.
Sheet1 of the spreadsheet contains the
named range DATA, which consists of the example
data set in worksheet cells A4 through C28.

Model Data in Worksheet
To perform regression and curve fitting, execute the specified Spreadsheet Link functions in worksheet cells.
Execute the Spreadsheet Link function that copies the sample data set to the MATLAB workspace by double-clicking the cell
E5and pressing Enter. The data set contains 25 observations of three variables. There is a strong linear dependence among the observations. In fact, they are close to being scalar multiples of each other.Execute the functions in cells
E8,E9, andE10. The Spreadsheet Link functions in these cells regress the third column of data on the other two columns, and create:A single vector
ycontaining the third-column dataA three-column matrix
A, which consists of a column of 1s followed by the rest of the data
Execute the function in cell
E13. This function calculates the regression coefficients by using the MATLAB back slash(\)operation to solve the overdetermined system of linear equations,A*beta = y.Execute the function in cell
E16. MATLAB matrix-vector multiplication produces the regressed result,fit.Execute the functions in cells
E19,E20, andE21. These functions:Compare the original data with
fit.Sort the data in increasing order and apply the same permutation to
fit.Create a scalar for the number of observations.
Execute the functions in cells
E24andE25. Fit a polynomial equation to the data for a fifth-degree polynomial. The MATLABpolyfitfunction automates setting up a system of simultaneous linear equations and solutions for the coefficients. Thepolyvalfunction then evaluates the resulting polynomial at each data point to check the goodness of the fitnewfit.Execute the function in cell
E28. The MATLABplotfunction graphs the original data (blue circles), the regressed resultfit(dashed red line), and the polynomial result (solid green line).
Since the data is closely correlated, but not exactly linearly dependent, the
fitcurve (dashed line) shows a close, but not exact, fit. The fifth-degree polynomial curvenewfitis a more accurate mathematical model for the data.
Model Data Using VBA Macro
To model the data using a VBA macro, execute the Spreadsheet Link functions in a VBA macro.
In the
ExliSamp.xlsfile, click the Sheet2 tab. The worksheet for this example appears.
Cell
A4calls the macroCurveFit, which you can examine in the Microsoft Visual Basic environment.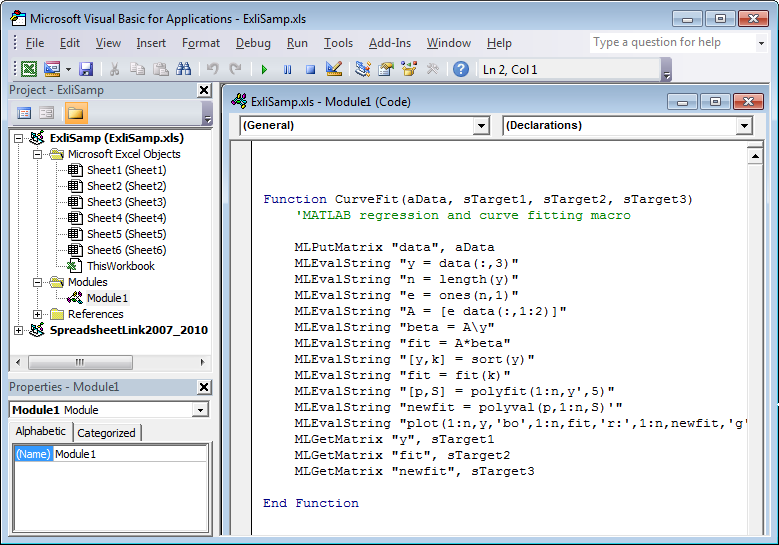
While this module is open, ensure that the Spreadsheet Link add-in is enabled. To enable it, see Add-In Setup. After the add-in is enabled, the Project Explorer lists it under the References folder.
Execute the
CurveFitmacro by double-clicking the cellA4and pressing Enter. The macro runs the Spreadsheet Link functions. When the macro finishes, the input and output data appears in worksheet cellsA7:C31.Column A contains the original data
y(sorted).Column B contains the corresponding regressed data
fit.Column C contains the polynomial data
newfit.

See Also
MLGetMatrix | MLPutMatrix | MLEvalString | polyfit | polyval | plot