Satellite
Description
Satellite defines a satellite in satellite scenario object.
Creation
You can create Satellite objects using the satellite function of satelliteScenario
object.
Properties
You can set this property only when calling the satellite function. After you call satellite function, this property is read-only.
Satellite name, specified as a comma-separated pair consisting of 'Name' and a string scalar, string vector, character vector or a cell array of character vectors.
If only one satellite is added, specify
Nameas a string scalar or a character vector.If multiple satellites are added, specify
Nameas a string scalar, character vector, string vector or a cell array of character vectors. All satellites added as a string scalar or a character vector are assigned the same specified name. The number of elements in the string vector or cell array of character vector must equal the number of satellites being added. Each satellite is assigned the corresponding name from the vector or cell array.
The default value when satellite is added to the satellite scenario using
Keplerian orbital elements, TLE file — "Satellite ID", where
IDis assigned by the satellite scenario.SEM almanac file or RINEX GPS navigation data — "PRN:prnValue", where prnValue is an integer denoting the pseudorandom noise code of the satellite as specified in the SEM almanac file.
RINEX Galileo navigation data — "GAL Sat IF: id", where "id" is the satellite ID of the Galileo satellite defined in the RINEX navigation data.
Timetable - Variable names of the timetable object
Timeseries - Name of the timeseries object if populated, otherwise "Satellite ID", where ID is assigned by satellite scenario.
Data Types: string
This property is set internally by the simulator and is read-only.
Satellite ID assigned by the simulator, specified as a positive scalar.
You can set this property only when calling
the conicalSensor. After you
call the conicalSensor function, this property is read-only.
Conical sensors attached to the Satellite, specified as a row vector of conical sensors.
You can set this property only when calling transmitter function. After you call the
transmitter function, this property is read-only.
Transmitters attached to the Satellite, specified as a row vector of Transmitter
objects.
You can set this property only when calling access.
After you call access, this property is
read-only.
Access analysis objects, specified as a row vector of
Access objects.
You can set this property only when calling groundTrack. After you
call groundTrack, this
property is read-only.
Ground track of the Satellite, specified as a row vector of GroundTrack
objects.
You can set this property only when calling coordinateAxes.
After you call coordinateAxes,
this property is read-only.
Coordinate axes triad graphic object, specified as CoordinateAxes
object.
You can set this property on satellite object creation and then this
property becomes read-only.
Name of the orbit propagator used for propagating the satellite position and velocity, specified as one of these options.
If you specify the satellite using timetable, table,
timeseries, ortscollection, theOrbitPropagatorvalue is"ephemeris".If you specify the satellite using a SEM almanac file or RINEX data containing a GPS navigation message, the
OrbitPropagatorvalue can take one of these options."gps"(default)"sgp4""sdp4""two-body-keplerian""numerical"
If you specify the satellite using the RINEX data containing a Galileo navigation message, the
OrbitPropagatorvalue can take one of these options."galileo"(default)"sgp4""sdp4""two-body-keplerian""numerical"
If you specify the satellite is added using Keplerian elements,
OrbitPropagatorvalue can take one of these options."two-body-keplerian""sgp4""sdp4""numerical"
Additionally, if semimajor axis is negative,
OrbitPropagatorvalue can only be"numerical". If semimajor axis is positive, default value is"sgp4"for periods less than 225 min and"sdp4"for periods greater than or equal to 225 minutes.If you specify the satellite using a TLE or OMM file, the
OrbitPropagatorvalue can take one of these options."two-body-keplerian""sgp4""sdp4""numerical"
If the orbital period is less than 225 minutes, the default
OrbitPropagatorvalue is"sgp4". Otherwise, the defaultOrbitPropagatorvalue is"sdp4".If you specify the satellite using
Keplerianelements, theOrbitPropagatorvalue can take one of these options."two-body-keplerian""sgp4""sdp4"
If the RINEX data contains both valid GPS and Galileo navigation messages, you cannot
specify OrbitPropagator as "gps" or
"galileo" using a name-value argument. However, you can still specify it
as "two-body-keplerian", "sgp4",
"sdp4", or "numerical".
Color of the marker, specified as a comma-separated pair consisting of
'MarkerColor' and either an RGB triplet or a string or
character vector of a color name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red"
|
"r"
|
[1 0 0]
|
"#FF0000"
|
|
"green"
|
"g"
|
[0 1 0]
|
"#00FF00"
|
|
"blue"
|
"b"
|
[0 0 1]
|
"#0000FF"
|
|
"cyan"
|
"c"
|
[0 1 1]
|
"#00FFFF"
|
|
"magenta"
|
"m"
|
[1 0 1]
|
"#FF00FF"
|
|
"yellow"
|
"y"
|
[1 1 0]
|
"#FFFF00"
|
|
"black"
|
"k"
|
[0 0 0]
|
"#000000"
|
|
"white"
|
"w"
|
[1 1 1]
|
"#FFFFFF"
|
|
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB® uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410]
|
"#0072BD"
|
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980]
|
"#D95319"
|
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250]
|
"#EDB120"
|
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560]
|
"#7E2F8E"
|
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880]
|
"#77AC30"
|
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330]
|
"#4DBEEE"
|
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840]
|
"#A2142F"
|
|
Size of the marker, specified as a comma-separated pair consisting of
'MarkerSize' and a real positive scalar less than 30. The unit
is in pixels.
State of Satellite label visibility, specified as a
comma-separated pair consisting of
'ShowLabel' and numerical or
logical value of 1
(true) or 0
(false).
Data Types: logical
Font color of the Satellitelabel, specified as a comma-separated pair consisting of
'LabelFontColor' and either an RGB triplet or a string or
character vector of a color name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red"
|
"r"
|
[1 0 0]
|
"#FF0000"
|
|
"green"
|
"g"
|
[0 1 0]
|
"#00FF00"
|
|
"blue"
|
"b"
|
[0 0 1]
|
"#0000FF"
|
|
"cyan"
|
"c"
|
[0 1 1]
|
"#00FFFF"
|
|
"magenta"
|
"m"
|
[1 0 1]
|
"#FF00FF"
|
|
"yellow"
|
"y"
|
[1 1 0]
|
"#FFFF00"
|
|
"black"
|
"k"
|
[0 0 0]
|
"#000000"
|
|
"white"
|
"w"
|
[1 1 1]
|
"#FFFFFF"
|
|
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410]
|
"#0072BD"
|
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980]
|
"#D95319"
|
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250]
|
"#EDB120"
|
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560]
|
"#7E2F8E"
|
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880]
|
"#77AC30"
|
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330]
|
"#4DBEEE"
|
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840]
|
"#A2142F"
|
|
Font size of the Satellite label, specified as a comma-separated pair consisting of
'LabelFontSize' and a positive scalar in the range [6
30].
Name of the visual 3-D model file that you want to render in the viewer, specified as a string with .GLTF, .GLB, or .STL extension. For GLB and GLTF models, gITF uses a right-hand coordinate system. gITF defines +Y as up, and +Z as forward, and -X as right. A gITF asset faces +Z. For more information, see https://registry.khronos.org/glTF/specs/2.0/glTF-2.0.html#coordinate-system-and-units. The mesh of the GLB is in meters.

Data Types: string
Linear scaling of the visual 3-D model rendered in the viewer, specified as a nonnegative integer. The scaling assumes that the GLB model is in meters.
Data Types: double
Object Functions
access | Add access analysis objects to satellite scenario |
aer | Calculate azimuth angle, elevation angle, and range of another satellite or ground station in NED frame |
dopplershift | Calculate Doppler shift at target asset in satellite scenario |
latency | Calculate propagation delay from one asset to another asset |
conicalSensor | Add conical sensor to satellite scenario |
gimbal | Add gimbal to satellite, platform, or ground station |
groundTrack | Add ground track object to satellite or platform in scenario |
orbitalElements | Orbital elements of satellites in scenario |
coordinateAxes | Visualize coordinate axes triad of satellite scenario assets |
pointAt | Point satellite at target |
receiver | Add receiver to satellite scenario |
transmitter | Add transmitter to satellite scenario |
states | Obtain position and velocity of satellite or platform |
show | Show object in satellite scenario viewer |
hide | Hide satellite scenario entity from viewer |
Examples
Create a satellite scenario object.
startTime = datetime(2020,5,5,0,0,0);
stopTime = startTime + days(1);
sampleTime = 60; %seconds
sc = satelliteScenario(startTime,stopTime,sampleTime);Add a satellite from a TLE file to the scenario.
tleFile = "eccentricOrbitSatellite.tle"; sat1 = satellite(sc,tleFile,"Name","Sat1")
sat1 =
Satellite with properties:
Name: Sat1
ID: 1
ConicalSensors: [1x0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.ConicalSensor]
Gimbals: [1x0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Gimbal]
Transmitters: [1x0 satcom.satellitescenario.Transmitter]
Receivers: [1x0 satcom.satellitescenario.Receiver]
Accesses: [1x0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Access]
GroundTrack: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.GroundTrack]
Orbit: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Orbit]
OrbitPropagator: sdp4
MarkerColor: [0.059 1 1]
MarkerSize: 6
ShowLabel: true
LabelFontColor: [1 1 1]
LabelFontSize: 15
Add a satellite from Keplerian elements to the scenario and specify its orbit propagator to be "two-body-keplerian".
semiMajorAxis = 6878137; %m eccentricity = 0; inclination = 20; %degrees rightAscensionOfAscendingNode = 0; %degrees argumentOfPeriapsis = 0; %degrees trueAnomaly = 0; %degrees sat2 = satellite(sc,semiMajorAxis,eccentricity,inclination,rightAscensionOfAscendingNode,... argumentOfPeriapsis,trueAnomaly,"OrbitPropagator","two-body-keplerian","Name","Sat2")
sat2 =
Satellite with properties:
Name: Sat2
ID: 2
ConicalSensors: [1x0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.ConicalSensor]
Gimbals: [1x0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Gimbal]
Transmitters: [1x0 satcom.satellitescenario.Transmitter]
Receivers: [1x0 satcom.satellitescenario.Receiver]
Accesses: [1x0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Access]
GroundTrack: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.GroundTrack]
Orbit: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Orbit]
OrbitPropagator: two-body-keplerian
MarkerColor: [0.059 1 1]
MarkerSize: 6
ShowLabel: true
LabelFontColor: [1 1 1]
LabelFontSize: 15
Add access analysis between the two satellites.
ac = access(sat1,sat2);
Determine the times when there is line of sight between the two satellites.
accessIntervals(ac)
ans=15×8 table
Source Target IntervalNumber StartTime EndTime Duration StartOrbit EndOrbit
______ ______ ______________ ____________________ ____________________ ________ __________ ________
"Sat1" "Sat2" 1 05-May-2020 00:09:00 05-May-2020 01:08:00 3540 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 2 05-May-2020 01:50:00 05-May-2020 02:47:00 3420 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 3 05-May-2020 03:45:00 05-May-2020 04:05:00 1200 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 4 05-May-2020 04:32:00 05-May-2020 05:26:00 3240 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 5 05-May-2020 06:13:00 05-May-2020 07:10:00 3420 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 6 05-May-2020 07:52:00 05-May-2020 08:50:00 3480 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 7 05-May-2020 09:30:00 05-May-2020 10:29:00 3540 1 1
"Sat1" "Sat2" 8 05-May-2020 11:09:00 05-May-2020 12:07:00 3480 1 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 9 05-May-2020 12:48:00 05-May-2020 13:46:00 3480 2 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 10 05-May-2020 14:31:00 05-May-2020 15:27:00 3360 2 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 11 05-May-2020 17:12:00 05-May-2020 18:08:00 3360 2 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 12 05-May-2020 18:52:00 05-May-2020 19:49:00 3420 2 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 13 05-May-2020 20:30:00 05-May-2020 21:29:00 3540 2 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 14 05-May-2020 22:08:00 05-May-2020 23:07:00 3540 2 2
"Sat1" "Sat2" 15 05-May-2020 23:47:00 06-May-2020 00:00:00 780 2 2
Visualize the line of sight between the satellites.
play(sc);
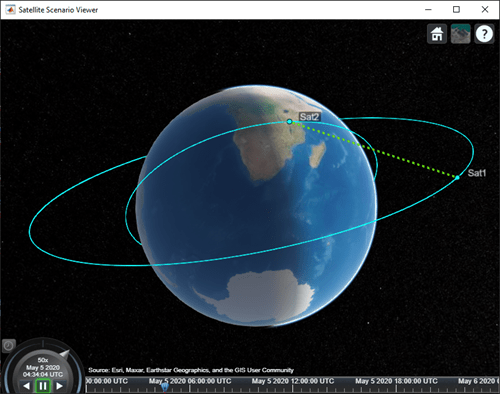
Set up the satellite scenario.
startTime = datetime(2021,8,5);
stopTime = startTime + days(1);
sampleTime = 60; % seconds
sc = satelliteScenario(startTime,stopTime,sampleTime);Add satellites to the scenario from a SEM almanac file.
sat = satellite(sc,"gpsAlmanac.txt","OrbitPropagator","gps");
Visualize the GPS constellation.
v = satelliteScenarioViewer(sc);
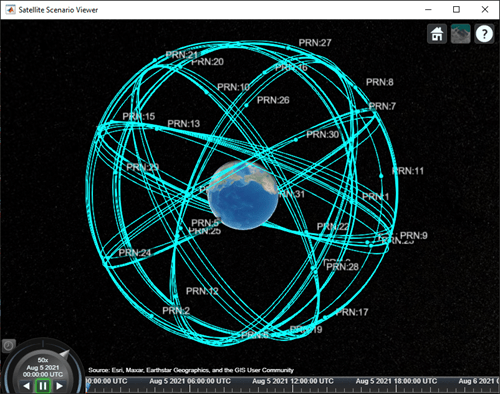
References
[1] Hoots, Felix R., and Ronald L. Roehrich. Models for propagation of NORAD element sets. Aerospace Defense Command Peterson AFB CO Office of Astrodynamics, 1980.
[2] Vallado, David, et al. “Revisiting Spacetrack Report #3.” AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006, https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2006-6753
Version History
Introduced in R2021a
See Also
Objects
satelliteScenario|GroundStation|Access|satelliteScenarioViewer|Eclipse(Aerospace Toolbox) |Platform
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)