ClassificationDiscriminant Predict
Libraries:
Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox /
Classification
Description
The ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block classifies observations using
a discriminant analysis classification object (ClassificationDiscriminant) for multiclass classification.
Import a trained classification object into the block by specifying the name of a workspace variable that contains the object. The input port x receives an observation (predictor data), and the output port label returns a predicted class label for the observation. The optional output port score returns the predicted class scores or posterior probabilities. The optional output port cost returns the expected classification costs.
Examples
This example shows how to use the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block for label prediction in Simulink®. The block accepts an observation (predictor data) and returns the predicted class label, class score, and expected classification cost for the observation using the trained discriminant analysis classification model. To complete this example, you can use the provided Simulink model, or create a new model.
Train Classification Model
Load the humanactivity data set. This data set contains 24,075 observations of five physical human activities: Sitting, Standing, Walking, Running, and Dancing. Each observation has 60 features extracted from acceleration data measured by smartphone accelerometer sensors.
load humanactivityCreate the predictor X as a numeric matrix that contains 60 features for 24,075 observations. Create the class labels Y as a numeric vector that contains the activity IDs in integers: 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 representing Sitting, Standing, Walking, Running, and Dancing, respectively.
X = feat; Y = actid;
Randomly partition observations into a training set and a test set with stratification using the class information in Y. Use approximately 80% of the observations to train a discriminant analysis model, and 20% of the observations to test the performance of the trained model on new data.
rng(0,"twister") % For reproducibility of the partition cv = cvpartition(Y,"Holdout",0.20);
Extract the training and test indices.
trainingInds = training(cv); testInds = test(cv);
Specify the training and test data sets.
XTrain = X(trainingInds,:); YTrain = Y(trainingInds); XTest = X(testInds,:); YTest = Y(testInds);
Train a discriminant analysis classification model by passing the training data XTrain and YTrain to the fitcdiscr function.
daMdl = fitcdiscr(XTrain,YTrain);
daMdl is a trained ClassificationDiscriminant model. You can use dot notation to access the properties of daMdl. For example, you can enter daMdl.ModelParameters to get more information about the trained model parameters.
Open Provided Simulink Model
This example provides the Simulink model slexClassificationDAPredictExample.slx, which includes the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block. You can open the Simulink model or create a new model as described in the next section.
Open the Simulink model slexClassificationDAPredictExample.slx.
open_system("slexClassificationDAPredictExample")
When you open the Simulink model, the software runs the code in the PreLoadFcn callback function before loading the model. The PreLoadFcn callback function of slexClassificationDAPredictExample includes code to check if your workspace contains the daMdl variable for the trained model. If the workspace does not contain the variable, PreLoadFcn loads the sample data, trains the discriminant analysis classification model, and creates an input signal for the Simulink model. To view the callback function, in the Setup section on the Modeling tab, click Model Settings and select Model Properties. Then, on the Callbacks tab, select the PreLoadFcn callback function in the Model callbacks pane.
Create Simulink Model
To create a new Simulink model, open the Blank Model template and add the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block from the Classification section of the Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™ library.
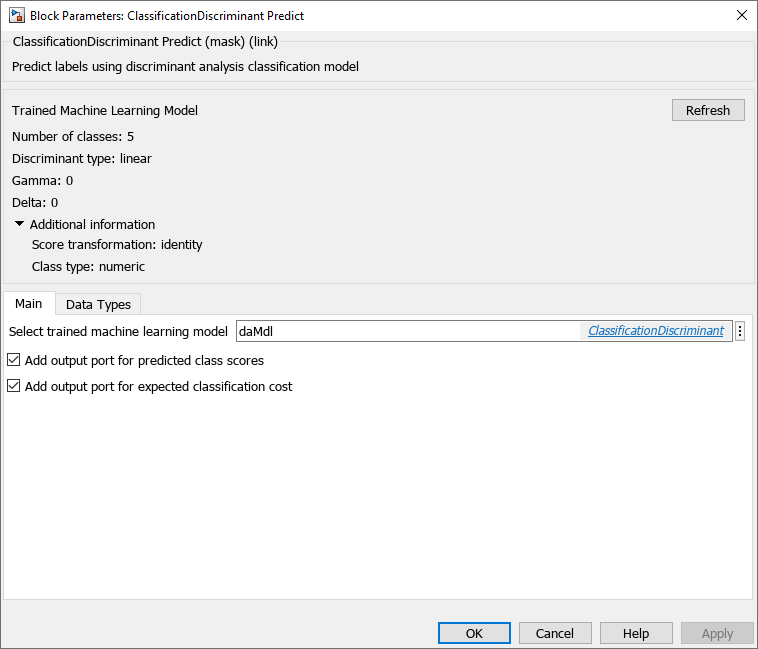
Double-click the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block to open the Block Parameters dialog box. Import a trained ClassificationDiscriminant model into the block by specifying the name of a workspace variable that contains the object. The default variable name is daMdl, which is the object you created at the command line.
Select the check box for Add output port for predicted class scores to add the second output port score, and select the check box for Add output port for expected classification cost to add the third output port cost. Click OK.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the settings of the trained model in the dialog box. The Trained Machine Learning Model section of the dialog box displays the options used to train the model daMdl.
Add one Inport block and three Outport blocks, and connect them to the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block.
The ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block expects an observation containing 60 predictor values, because the model was trained using a data set with 60 predictor variables. Double-click the Inport block, and set Port dimensions to 60 on the Signal Attributes tab. To specify that the output signals have the same length as the input signal, set Sample time to 1 on the Execution tab of the Inport dialog box. Click OK.
At the command line, create an input signal in the form of a structure array for the Simulink model. The structure array must contain these fields:
time— The points in time at which the observations enter the model. The orientation must correspond to the observations in the predictor data. In this example,timemust be a column vector.signals— A 1-by-1 structure array describing the input data and containing the fieldsvaluesanddimensions, wherevaluesis a matrix of predictor data, anddimensionsis the number of predictor variables.
Create an appropriate structure array for future predictions.
modelInput.time = (0:length(YTest)-1)'; modelInput.signals(1).values = XTest; modelInput.signals(1).dimensions = size(XTest,2);
Import the signal data from the workspace:
Open the Configuration Parameters dialog box in Simulink. In the Setup section of the Modeling tab, click the top half of the Model Settings button.
In the Data Import/Export pane, select the Input check box and enter
modelInputin the adjacent text box.In the Solver pane, under Simulation time, set Stop time to
modelInput.time(end). Under Solver selection, set Type toFixed-step, and set Solver todiscrete (no continuous states). These settings enable the model to run the simulation for each query point inmodelInput. Click OK.
For more details, see Load Signal Data for Simulation (Simulink).
Save the model as slexClassificationDAPredictExample.slx in Simulink.
Simulate Model
Simulate the Simulink model and export the simulation outputs to the workspace. When the Inport block detects an observation, it places the observation into the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block. You can use the Simulation Data Inspector (Simulink) to view the logged data of an Outport block.
simOut = sim("slexClassificationDAPredictExample");Determine the simulated classification labels.
outputs = simOut.yout;
sim_label = outputs.get("label").Values.Data;Create a confusion matrix chart from the true labels (YTest) and the labels predicted by the Simulink model (sim_label).
confusionchart(string(YTest),string(sim_label))

Large values on the diagonal indicate accurate predictions for the corresponding class.
Ports
Input
Predictor data, specified as a row or column vector of one observation.
The variables in x must have the same order as the predictor variables that trained the model specified by Select trained machine learning model.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Output
Predicted class label, returned as a scalar. The predicted class is the class that
minimizes the expected classification cost. For more details, see the More About section of the
predict object function.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated
Predicted class scores or posterior probabilities, returned as a row vector of
size 1-by-k, where k is the number of classes in
the discriminant analysis model. The classification score Score(i)
represents the posterior probability that the observation in x
belongs to class i.
To check the order of the classes, use the ClassNames
property of the discriminant analysis model specified by Select trained machine
learning model.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the check box for Add output port for predicted class scores on the Main tab of the Block Parameters dialog box.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Expected classification costs, returned as a row vector of size
1-by-k, where k is the number of classes in
the discriminant analysis model. The classification cost Cost(i)
represents the cost of classifying the observation in x to class
i.
To check the order of the classes, use the ClassNames
property of the discriminant analysis model specified by Select trained machine
learning model.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the check box for Add output port for expected classification cost on the Main tab of the Block Parameters dialog box.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Parameters
To edit block parameters interactively, use the Property Inspector. From the Simulink® Toolstrip, on the Simulation tab, in the Prepare gallery, select Property Inspector.
Main
Specify the name of a workspace variable that contains a ClassificationDiscriminant object.
When you train the model by using fitcdiscr, the following restrictions apply:
The predictor data cannot include categorical predictors (
logical,categorical,char,string, orcell). If you supply training data in a table, the predictors must be numeric (doubleorsingle). To include categorical predictors in a model, preprocess them by usingdummyvarbefore fitting the model.The value of the
ScoreTransformname-value argument cannot be"invlogit"or an anonymous function.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
TrainedLearner |
| Type: workspace variable |
Values:
ClassificationDiscriminant object |
Default:
"daMdl" |
Select the check box to include the output port score in the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ShowOutputScore |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Select the check box to include the output port cost in the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ShowOutputCost |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Data Types
Fixed-Point Operational Parameters
Specify the rounding mode for fixed-point operations. For more information, see Rounding Modes (Fixed-Point Designer).
Block parameters always round to the nearest representable value. To control the rounding of a block parameter, enter an expression into the mask field using a MATLAB® rounding function.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
RndMeth |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"Ceiling" | "Convergent" | "Floor" | "Nearest" | "Round" | "Simplest" |
"Zero" |
Default:
"Floor" |
Specify whether overflows saturate or wrap.
| Action | Rationale | Impact on Overflows | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Select this check box
( | Your model has possible overflow, and you want explicit saturation protection in the generated code. | Overflows saturate to either the minimum or maximum value that the data type can represent. | The maximum value that the |
Clear this check box
( | You want to optimize the efficiency of your generated code. You want to avoid overspecifying how a block handles out-of-range signals. For more information, see Troubleshoot Signal Range Errors (Simulink). | Overflows wrap to the appropriate value that the data type can represent. | The maximum value that the |
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
SaturateOnIntegerOverflow |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Select this parameter to prevent the fixed-point tools from overriding the data type you specify for the block. For more information, see Use Lock Output Data Type Setting (Fixed-Point Designer).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
LockScale |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Data Type
Specify the data type for the label output. The type can be
inherited, specified as an enumerated data type, or
expressed as a data type object such as Simulink.NumericType.
The supported data types depend on the labels used in the model specified by Select trained machine learning model.
If the model uses numeric or logical labels, the supported data types are
Inherit: Inherit via back propagation(default),double,single,half,int8,uint8,int16,uint16,int32,uint32,int64,uint64,boolean, fixed point, and a data type object.If the model uses nonnumeric labels, the supported data types are
Inherit: auto(default),Enum: <class name>, and a data type object.
When you select an inherited option, the software behaves as follows:
Inherit: Inherit via back propagation(default for numeric and logical labels) — Simulink automatically determines the Label data type of the block during data type propagation (see Data Type Propagation (Simulink)). In this case, the block uses the data type of a downstream block or signal object.Inherit: auto(default for nonnumeric labels) — The block uses an autodefined enumerated data type variable. For example, suppose the workspace variable name specified by Select trained machine learning model ismyMdl, and the class labels areclass 1andclass 2. Then, the corresponding label values aremyMdl_enumLabels.class_1andmyMdl_enumLabels.class_2. The block converts the class labels to valid MATLAB identifiers by using thematlab.lang.makeValidNamefunction.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type assistant
button ![]() to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
LabelDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector or string |
Values: "Inherit: Inherit via back
propagation" | "Inherit: auto" |
"double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)"
| "Enum: <class name>" | "<data type
expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: Inherit via
back propagation" (for numeric and logical labels) |
"Inherit: auto" (for nonnumeric labels) |
Specify the lower value of the label output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Label data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual label output signal. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Dependencies
You can specify this parameter only if the model specified by Select trained machine learning model uses numeric labels.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
LabelOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the label output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Label data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual label output signal. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Dependencies
You can specify this parameter only if the model specified by Select trained machine learning model uses numeric labels.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
LabelOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the score output. The type can be
inherited, specified directly, or expressed as a data type object such as
Simulink.NumericType.
When you select Inherit: auto, the block uses a rule that
inherits a data
type.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type assistant
button ![]() to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ScoreDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector or string |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)"
| "<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit:
auto" |
Specify the lower value of the score output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Score data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual score output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ScoreOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the score output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Score data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual score output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ScoreOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the internal untransformed scores. The type can be inherited, specified directly, or expressed as a data type object such as Simulink.NumericType.
When you select Inherit: auto, the block uses a rule that inherits a data type.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type assistant
button ![]() to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Dependencies
You can specify this parameter only if the model specified by Select trained
machine learning model uses a score transformation other than
"none" (default, same as "identity").
If the model uses no score transformations (
"none"or"identity"), then you can specify the score data type by using Score data type.If the model uses a score transformation other than
"none"or"identity", then you can specify the data type of untransformed raw scores by using this parameter. To specify the data type of transformed scores, use Score data type.
You can change the score transformation option by specifying the
ScoreTransform name-value argument during training, or by
modifying the ScoreTransform property after training.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: RawScoreDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto" |
"double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)"
| "<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto" |
Specify the lower value of the untransformed score range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Raw score data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual untransformed score signal.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
RawScoreOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the untransformed score range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Raw score data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual untransformed score signal.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
RawScoreOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the cost output. The type can be inherited, specified directly, or expressed as a data type object such as Simulink.NumericType.
When you select Inherit: auto, the block uses a rule that inherits a data type.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type assistant
button ![]() to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: CostDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector or string |
Values: "Inherit: auto" | "double" | "single" | "half" | "int8" | "uint8" | "int16" | "uint16" | "int32" | "uint32" | "int64" | "uint64" | "boolean" | "fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" | "<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto" |
Specify the lower value of the cost output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Estimated cost data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual cost signal. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: CostOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" | scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the cost output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Estimated cost data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual cost signal. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: CostOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" | scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Additional Data Types
Specify the data type of the Mahalanobis distance metric. The type can be
inherited, specified directly, or expressed as a data type object such as
Simulink.NumericType.
When you select Inherit: auto, the block uses a rule
that inherits a data type.
Click the Show data type assistant
button ![]() to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type Assistant,
which helps you set the data type attributes. For more information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Note
The Mahalanobis distance data type parameter specifies
the data type of the distance metric used internally by the block. For more
information, see mahal.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
DistanceDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" |
"<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit:
auto" |
Specify the lower value of the distance range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Mahalanobis distance data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual distance signal.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
DistanceOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the distance range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Mahalanobis distance data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual distance signal.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
DistanceOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
More About
The data types of internal model parameters are
synchronized to the data type of the enabled score output port. If the
score output port is not enabled, the model parameter data types
are synchronized to other internal data types.
Alternative Functionality
You can use a MATLAB Function (Simulink) block with the predict object function of a discriminant analysis classification object
(ClassificationDiscriminant). For an example, see Predict Class Labels Using MATLAB Function Block.
When deciding whether to use the ClassificationDiscriminant Predict block
in the Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™ library or a MATLAB Function block with the predict function, consider the
following:
If you use the Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox library block, you can use the Fixed-Point Tool (Fixed-Point Designer) to convert a floating-point model to fixed point.
Support for variable-size arrays must be enabled for a MATLAB Function block with the
predictfunction.If you use a MATLAB Function block, you can use MATLAB functions for preprocessing or post-processing before or after predictions in the same MATLAB Function block.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Fixed-Point Conversion
Design and simulate fixed-point systems using Fixed-Point Designer™.
Version History
Introduced in R2024a
See Also
Blocks
- ClassificationSVM Predict | ClassificationTree Predict | ClassificationEnsemble Predict | ClassificationNeuralNetwork Predict | ClassificationNaiveBayes Predict | ClassificationKNN Predict
Functions
Objects
Topics
- Predict Class Labels Using MATLAB Function Block
- Predict Class Labels Using ClassificationNaiveBayes Predict Block
- Predict Class Labels Using ClassificationSVM Predict Block
- Predict Class Labels Using ClassificationEnsemble Predict Block
- Predict Class Labels Using ClassificationTree Predict Block
- Predict Class Labels Using ClassificationNeuralNetwork Predict Block
- Predict Class Labels Using ClassificationKNN Predict Block
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)