drawassisted
Create customizable freehand ROI with assistance from object edges
Description
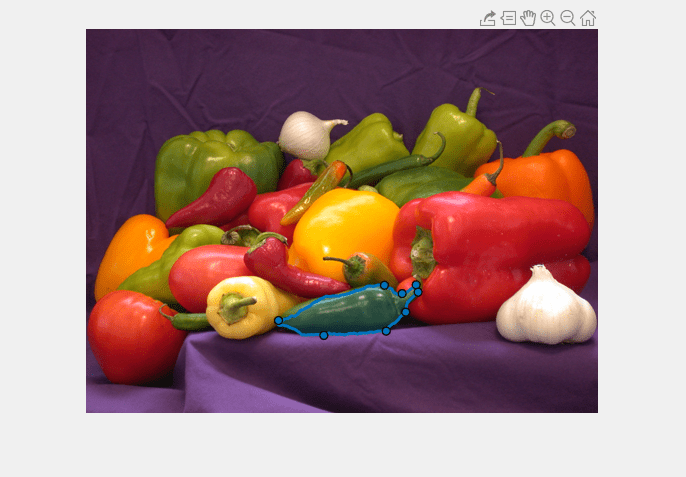
The drawassisted function creates an AssistedFreehand
object that specifies the shape and position of a freehand region of interest (ROI) that
follows the contours of objects in the image. You can create the ROI interactively by drawing
the ROI over an image using the mouse, or programmatically by using name-value arguments. You
can also specify the initial appearance and behavior of the ROI.
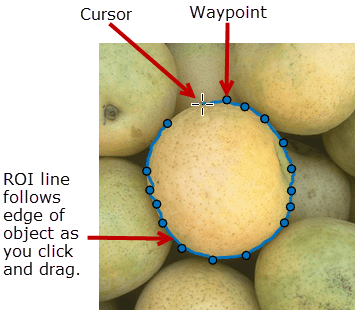
After you create the ROI, you can use object properties, object functions, and event notifications to customize the shape, position, appearance, and behavior of the ROI. For more information about using these capabilities, see Tips.
roi = drawassistedAssistedFreehand object and enables interactive drawing of the hand-drawn
region-of-interest (ROI) on the current axes. The AssistedFreehand ROI uses
the edges in the underlying image to "assist" you as you draw the shape.
To draw the ROI, position the pointer on the image, click and release to place the first vertex (waypoint), and then move the pointer to draw a line. As you move the pointer to draw the shape, the line follows the contours of edges in the underlying image automatically. As you draw, click to place vertices along the line. To finish the ROI and close the shape, double-click. For more information about using the ROI, including keyboard shortcuts and context menu options, see Tips.
roi = drawassisted(___,Name=Value)
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
Tips
This table describes how to perform common tasks with the
AssistedFreehandROI.Behavior Keyboard shortcut Remove the most recently added waypoint but keep drawing. Press Backspace. The function redraws the line from the previous waypoint to the current position of the pointer. You can only back up to the first waypoint you drew. Cancel drawing the ROI. Press Esc. The function returns a valid ROI object with an empty Positionproperty.Finish drawing (close) the ROI. Double-click, which adds a point at the pointer position and draws a line connecting this point to the first point drawn, closing the ROI.
Right-click, which draws a line connecting the last point to the first point drawn.
Position the pointer over the first point and click.
Press Enter, which draws a line connecting the last point to the first point drawn.
Resize (reshape) the ROI. Position pointer over a waypoint and then click and drag. No assistance (snapping to edges) is available in this mode.
Add a waypoint. Position the pointer on an edge of the ROI, right-click, and select Add Waypoint. You can also position the pointer on an edge of the ROI and double-click.
Remove a waypoint. Position the pointer on a waypoint, right-click, and select Remove Waypoint.
Move the ROI. Position the pointer over the ROI. The pointer changes to the fleur shape. Click and drag to move the ROI. Delete an ROI. Position the pointer on the ROI (not on a vertex), right-click, and select Delete Freehand from the context menu. You can also delete the ROI programmatically using the deletefunction.The
drawassistedfunction creates anAssistedFreehandobject. After you create the object, you can modify the shape, position, appearance, and behavior of the ROI by using these object capabilities.Capability Support Object properties ROI objects have properties that specify their shape, position, appearance, and behavior. After you create the ROI object, change properties using dot notation.
For example, to change the color of the
roito yellow, set itsColorproperty:roi.Color = 'yellow'Object functions ROI objects have object functions that operate on the ROIs. For example, if you want to pause the MATLAB command line after creating an ROI, use the waitfunction.Event notifications ROI objects can notify your code when certain events occur, such as when the ROI is clicked or when the ROI is being moved. To receive event notifications, set up listeners. When the ROI notifies your application through the listener, it returns data specific to the event. For example, with the
ROIMovedevent, the ROI object returns its previous position and its current position. You can specify a callback function that executes when an event occurs.For an example of using event listeners with the
AssistedFreehandobject, see Set Up Listener for AssistedFreehand Events.



