xsort
Sort states based on state partition
Syntax
Description
xsys = xsort(sys)x or q vector based on the state partition.
Signal-based connections and physical interfaces between model components gives rise to
differential algebraic equation (DAE) models where some internal signals and forces become
extra states. The StateInfo property of sparss and
mechss model
objects keeps track of the state partition into sub-components, interface variables, and
signal variables.
Examples
For this example, consider sparseSOSignal.mat that contains a sparse second-order model. Define an actuator, sensor, and controller and connect them together with the plant in a feedback loop.
Load the sparse matrices and create the mechss object.
load sparseSOSignal.mat plant = mechss(M,C,K,B,F,[],[],'Name','Plant');
Next, create an actuator and sensor using transfer functions.
act = tf(1,[1 0.5 3],'Name','Actuator'); sen = tf(1,[0.02 7],'Name','Sensor');
Create a PID controller object for the plant.
con = pid(1,1,0.1,0.01,'Name','Controller');
Use the feedback command to connect the plant, sensor, actuator, and controller in a feedback loop.
sys = feedback(sen*plant*act*con,1)
Sparse continuous-time second-order model with 1 outputs, 1 inputs, and 7111 degrees of freedom. Model Properties Use "spy" and "showStateInfo" to inspect model structure. Type "help mechssOptions" for available solver options for this model.
The resultant system sys is a mechss object since mechss objects take precedence over all other model object types.
Use showStateInfo to view the component and signal groups.
showStateInfo(sys)
The state groups are:
Type Name Size
-------------------------------
Component Sensor 1
Component Plant 7102
Signal 1
Component Actuator 2
Signal 1
Component Controller 2
Signal 1
Signal 1
Use xsort to sort the components and signals, and then view the component and signal groups.
sysSort = xsort(sys); showStateInfo(sysSort)
The state groups are:
Type Name Size
-------------------------------
Component Sensor 1
Component Plant 7102
Component Actuator 2
Component Controller 2
Signal 4
Observe that the components are now ordered before the signal partition. The signals are now sorted and grouped together in a single partition.
You can also visualize the sparsity pattern of the resultant system using spy.
spy(sysSort)

For this example, consider a structural model that consists of two square plates connected with pillars at each vertex as depicted in the figure below. The lower plate is attached rigidly to the ground while the pillars are attached rigidly to each vertex of the square plate.
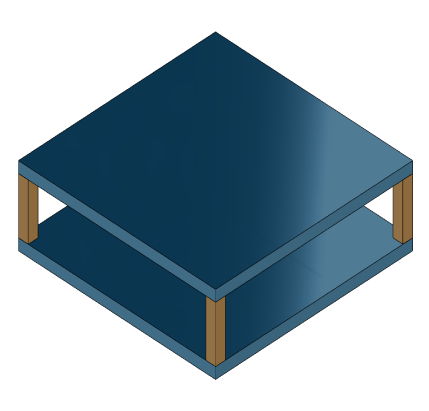
Load the finite element model matrices contained in platePillarModel.mat and create the sparse second-order model representing the above system.
load('platePillarModel.mat') model = ... mechss(M1,[],K1,B1,F1,'Name','Plate1') + ... mechss(M2,[],K2,B2,F2,'Name','Plate2') + ... mechss(Mp,[],Kp,Bp,Fp,'Name','Pillar3') + ... mechss(Mp,[],Kp,Bp,Fp,'Name','Pillar4') + ... mechss(Mp,[],Kp,Bp,Fp,'Name','Pillar5') + ... mechss(Mp,[],Kp,Bp,Fp,'Name','Pillar6'); sys = model;
Use showStateInfo to examine the components of the mechss model object.
showStateInfo(sys)
The state groups are:
Type Name Size
----------------------------
Component Plate1 2646
Component Plate2 2646
Component Pillar3 132
Component Pillar4 132
Component Pillar5 132
Component Pillar6 132
Now, load the interfaced degree of freedom (DOF) index data from dofData.mat and use interface to create the physical connections between the two plates and the four pillars. dofs is a 6x7 cell array where the first two rows contain DOF index data for the first and second plates while the remaining four rows contain index data for the four pillars. By default, the function uses dual-assembly method of physical coupling.
load('dofData.mat','dofs') for i=3:6 sys = interface(sys,"Plate1",dofs{1,i},"Pillar"+i,dofs{i,1}); sys = interface(sys,"Plate2",dofs{2,i},"Pillar"+i,dofs{i,2}); end
Specify connection between the bottom plate and the ground.
sysConDual = interface(sys,"Plate2",dofs{2,7});Use showStateInfo to confirm the physical interfaces.
showStateInfo(sysConDual)
The state groups are:
Type Name Size
-----------------------------------
Component Plate1 2646
Component Plate2 2646
Component Pillar3 132
Component Pillar4 132
Component Pillar5 132
Component Pillar6 132
Interface Plate1-Pillar3 12
Interface Plate2-Pillar3 12
Interface Plate1-Pillar4 12
Interface Plate2-Pillar4 12
Interface Plate1-Pillar5 12
Interface Plate2-Pillar5 12
Interface Plate1-Pillar6 12
Interface Plate2-Pillar6 12
Interface Plate2-Ground 6
You can use spy to visualize the sparse matrices in the final model.
spy(sysConDual)

Now, specify physical connections using the primal-assembly method.
sys = model; for i=3:6 sys = interface(sys,"Plate1",dofs{1,i},"Pillar"+i,dofs{i,1},'primal'); sys = interface(sys,"Plate2",dofs{2,i},"Pillar"+i,dofs{i,2},'primal'); end sysConPrimal = interface(sys,"Plate2",dofs{2,7},'primal');
Use showStateInfo to confirm the physical interfaces.
showStateInfo(sysConPrimal)
The state groups are:
Type Name Size
----------------------------
Component Plate1 2646
Component Plate2 2640
Component Pillar3 108
Component Pillar4 108
Component Pillar5 108
Component Pillar6 108
Primal assembly eliminates half of the redundant DOFs associated with the shared set of DOFs in the global finite element mesh.
You can use spy to visualize the sparse matrices in the final model.
spy(sysConPrimal)

The data set for this example was provided by Victor Dolk from ASML.
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Sparse state-space model with sorted components, returned as a sparss or
mechss
model object. In the sorted xsys, all components appear first,
followed by the interfaces, and then followed by a single group of all internal signals.
The matrices and have the following block arrow structure:

Here, each diagonal block is a sub-component of sys. The last
row and column combines the Interface and Signal
groups to capture all couplings and connections between components.
Version History
Introduced in R2020b
See Also
sparss | mechss | interface | showStateInfo
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)