M-PSK Modulator Baseband
Modulate using M-ary phase shift keying
Libraries:
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
PSK
Communications Toolbox HDL Support /
Modulation /
PM
Description
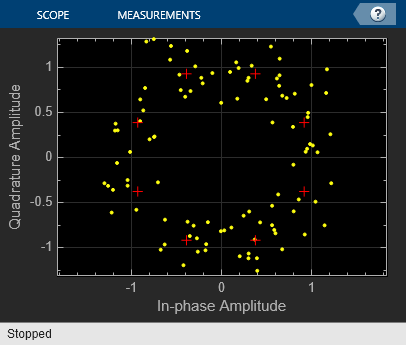
The M-PSK Modulator Baseband block modulates an input signal using M-ary phase shift keying (PSK) and returns a complex baseband output. The modulation order, M, which is equivalent to the number of points in the signal constellation, is determined by the M-ary number parameter. The block accepts scalar or column vector input signals.
Examples
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
More About
Algorithms
For higher-order PSK constellations, the complex baseband form for an M-ary PSK signal using binary-ordered symbol mapping is
When the input is configured for bits, groups of log2(M) bits represent the complex symbols for the configured symbol mapping. The mapping can be binary encoded, Gray encoded, or custom encoded.
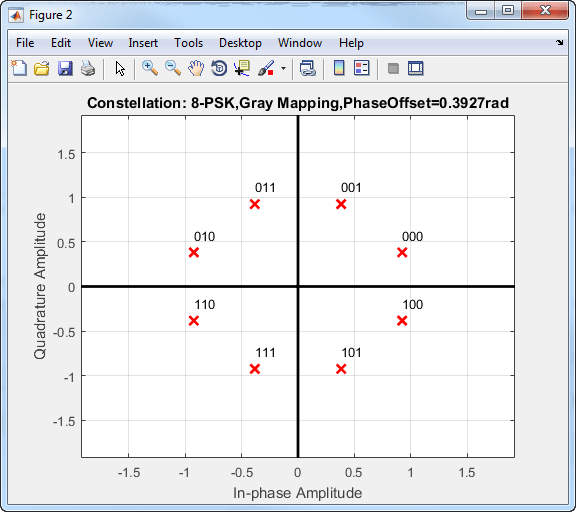
Gray coding has the advantage that only one bit changes between adjacent constellation points, which results in better bit error rate performance.
This 8-PSK constellation uses Gray-coded symbol mapping.
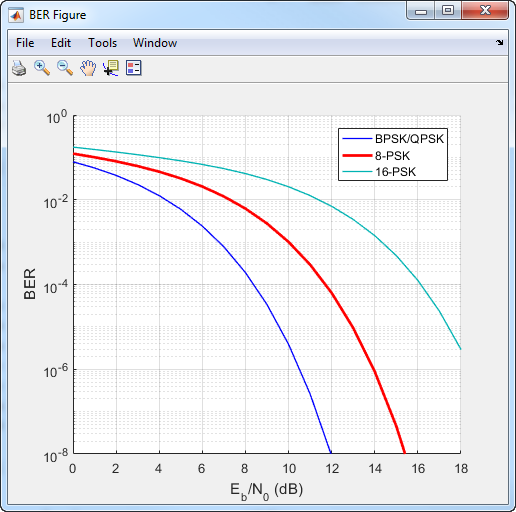
For modulation orders beyond 4, the bit error rate performance of PSK in AWGN worsens. In this bit error rate plot for Gray-coded mapping, the QPSK and BPSK curves overlap one another.
References
[1] Proakis, John G. Digital Communications. 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2001.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced before R2006a