2-D Stationary Wavelet Transform
This section takes you through the features of 2-D discrete stationary wavelet analysis using the Wavelet Toolbox™ software.
Analysis-Decomposition Function
| Function Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
Decomposition |
Synthesis-Reconstruction Function
| Function Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
Reconstruction |
The stationary wavelet decomposition structure is more tractable than the wavelet one. So, the utilities useful for the wavelet case are not necessary for the Stationary Wavelet Transform (SWT).
In this section, you'll learn to
Load an image
Analyze an image
Perform single-level and multilevel image decompositions and reconstructions
Denoise an image
2-D Analysis
In this example, we'll show how you can use 2-D stationary wavelet analysis to denoise an image.
Note
Instead of using image(I) to visualize the image
I, we use image(wcodemat(I)), which
displays a rescaled version of I leading to a clearer
presentation of the details and approximations (see the wcodemat reference
page).
This example involves a image containing noise.
Load an image.
From the MATLAB® prompt, type
load noiswom whos
Name Size Bytes Class X96x9673728double arraymap255x36120double arrayFor the SWT, if a decomposition at level
kis needed,2^kmust divide evenly intosize(X,1)andsize(X,2). If your original image is not of correct size, you can use the functionwextendto extend it.Perform a single-level Stationary Wavelet Decomposition.
Perform a single-level decomposition of the image using the
db1wavelet. Type[swa,swh,swv,swd] = swt2(X,1,'db1');
This generates the coefficients matrices of the level-one approximation (
swa) and horizontal, vertical and diagonal details (swh,swv, andswd, respectively). Both are of size-the-image size. Typewhos
Name Size Bytes Class X96x9673728double arraymap255x36120double arrayswa96x9673728double arrayswh96x9673728double arrayswv96x9673728double arrayswd96x9673728double arrayDisplay the coefficients of approximation and details.
To display the coefficients of approximation and details at level 1, type
map = pink(size(map,1)); colormap(map) subplot(2,2,1), image(wcodemat(swa,192)); title('Approximation swa') subplot(2,2,2), image(wcodemat(swh,192)); title('Horiz. Detail swh') subplot(2,2,3), image(wcodemat(swv,192)); title('Vertical Detail swv') subplot(2,2,4), image(wcodemat(swd,192)); title('Diag. Detail swd');
Regenerate the image by Inverse Stationary Wavelet Transform.
To find the inverse transform, type
A0 = iswt2(swa,swh,swv,swd,'db1');
To check the perfect reconstruction, type
err = max(max(abs(X-A0))) err = 1.1369e-13Construct and display approximation and details from the coefficients.
To construct the level 1 approximation and details (
A1,H1,V1andD1) from the coefficientsswa,swh,swvandswd, typenulcfs = zeros(size(swa)); A1 = iswt2(swa,nulcfs,nulcfs,nulcfs,'db1'); H1 = iswt2(nulcfs,swh,nulcfs,nulcfs,'db1'); V1 = iswt2(nulcfs,nulcfs,swv,nulcfs,'db1'); D1 = iswt2(nulcfs,nulcfs,nulcfs,swd,'db1');
To display the approximation and details at level 1, type
colormap(map) subplot(2,2,1), image(wcodemat(A1,192)); title('Approximation A1') subplot(2,2,2), image(wcodemat(H1,192)); title('Horiz. Detail H1') subplot(2,2,3), image(wcodemat(V1,192)); title('Vertical Detail V1') subplot(2,2,4), image(wcodemat(D1,192)); title('Diag. Detail D1')
Perform a multilevel Stationary Wavelet Decomposition.
To perform a decomposition at level 3 of the image (again using the
db1wavelet), type[swa,swh,swv,swd] = swt2(X,3,'db1');
This generates the coefficients of the approximations at levels 1, 2, and 3 (
swa) and the coefficients of the details (swh,swvandswd). Observe that the matricesswa(:,:,i),swh(:,:,i),swv(:,:,i), andswd(:,:,i)for a given leveliare of size-the-image size. Typeclear A0 A1 D1 H1 V1 err nulcfs whos
Name Size Bytes Class X96x9673728double arraymap255x36120double arrayswa96x96x3221184double arrayswh96x96x3221184double arrayswv96x96x3221184double arrayswd96x96x3221184double arrayDisplay the coefficients of approximations and details.
To display the coefficients of approximations and details, type
colormap(map) kp = 0; for i = 1:3 subplot(3,4,kp+1), image(wcodemat(swa(:,:,i),192)); title(['Approx. cfs level ',num2str(i)]) subplot(3,4,kp+2), image(wcodemat(swh(:,:,i),192)); title(['Horiz. Det. cfs level ',num2str(i)]) subplot(3,4,kp+3), image(wcodemat(swv(:,:,i),192)); title(['Vert. Det. cfs level ',num2str(i)]) subplot(3,4,kp+4), image(wcodemat(swd(:,:,i),192)); title(['Diag. Det. cfs level ',num2str(i)]) kp = kp + 4; endReconstruct approximation at Level 3 and details from coefficients.
To reconstruct the approximation at level 3, type
mzero = zeros(size(swd)); A = mzero; A(:,:,3) = iswt2(swa,mzero,mzero,mzero,'db1');
To reconstruct the details at levels 1, 2 and 3, type
H = mzero; V = mzero; D = mzero; for i = 1:3 swcfs = mzero; swcfs(:,:,i) = swh(:,:,i); H(:,:,i) = iswt2(mzero,swcfs,mzero,mzero,'db1'); swcfs = mzero; swcfs(:,:,i) = swv(:,:,i); V(:,:,i) = iswt2(mzero,mzero,swcfs,mzero,'db1'); swcfs = mzero; swcfs(:,:,i) = swd(:,:,i); D(:,:,i) = iswt2(mzero,mzero,mzero,swcfs,'db1'); endReconstruct and display approximations at Levels 1, 2 from approximation at Level 3 and details at Levels 1, 2, and 3.
To reconstruct the approximations at levels 2 and 3, type
A(:,:,2) = A(:,:,3) + H(:,:,3) + V(:,:,3) + D(:,:,3); A(:,:,1) = A(:,:,2) + H(:,:,2) + V(:,:,2) + D(:,:,2);
To display the approximations and details at levels 1, 2, and 3, type
colormap(map) kp = 0; for i = 1:3 subplot(3,4,kp+1), image(wcodemat(A(:,:,i),192)); title(['Approx. level ',num2str(i)]) subplot(3,4,kp+2), image(wcodemat(H(:,:,i),192)); title(['Horiz. Det. level ',num2str(i)]) subplot(3,4,kp+3), image(wcodemat(V(:,:,i),192)); title(['Vert. Det. level ',num2str(i)]) subplot(3,4,kp+4), image(wcodemat(D(:,:,i),192)); title(['Diag. Det. level ',num2str(i)]) kp = kp + 4; endTo denoise an image, use the
ddencmpfunction to find the threshold value, use thewthreshfunction to perform the actual thresholding of the detail coefficients, and then use theiswt2function to obtain the denoised image.thr = 44.5; sorh = 's'; dswh = wthresh(swh,sorh,thr); dswv = wthresh(swv,sorh,thr); dswd = wthresh(swd,sorh,thr); clean = iswt2(swa,dswh,dswv,dswd,'db1');
To display both the original and denoised images, type
colormap(map) subplot(1,2,1), image(wcodemat(X,192)); title('Original image') subplot(1,2,2), image(wcodemat(clean,192)); title('denoised image')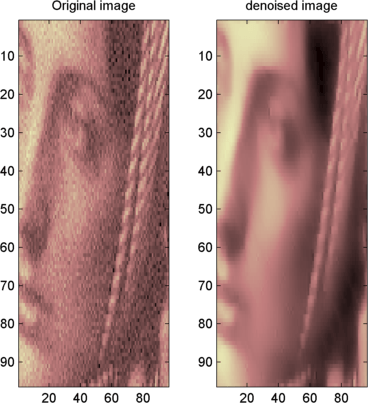
A second syntax can be used for the
swt2andiswt2functions, giving the same results:lev= 4; swc = swt2(X,lev,'db1'); swcden = swc; swcden(:,:,1:end-1) = wthresh(swcden(:,:,1:end-1),sorh,thr); clean = iswt2(swcden,'db1');
You obtain the same plot by using the plot commands in step 9 above.