Simplified Induction Motor
Induction motor powered by ideal AC supply
Libraries:
Simscape /
Electrical /
Electromechanical /
Asynchronous
Description
The Simplified Induction Motor block represents the electrical and torque characteristics of an induction motor powered by an ideal AC supply. The following figure shows the equivalent circuit model of the Simplified Induction Motor block.
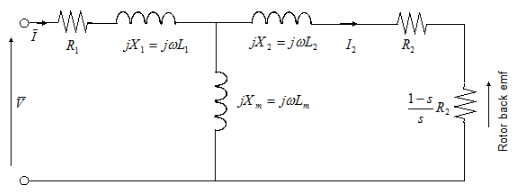
In the figure:
R1 is the stator resistance.
R2 is the rotor resistance with respect to the stator.
L1 is the stator inductance.
L2 is the rotor inductance with respect to the stator.
Lm is magnetizing inductance.
s is the rotor slip.
and are the sinusoidal supply voltage and current phasors.
Rotor slip s is defined in terms of the mechanical rotational speed , the number of pole pairs p, and the electrical supply frequency ω by
This means that the slip is one when starting, and zero when running synchronously with the supply frequency.
For an n-phase induction motor the torque-speed relationship is given by:
where:
Vrms is the line-neutral supply voltage for a star-configuration induction motor, and the line-to-line voltage for a delta-configuration induction motor.
n is the number of phases.
You can parameterize this block in terms of the preceding equivalent circuit model parameters or in terms of the motor ratings the block uses to derive these parameters.
This block produces a positive torque acting from the mechanical C to R ports.
Model Thermal Effects
You can expose thermal ports to model the effects of losses that convert power to heat. To expose the thermal ports, set the Modeling option parameter to either:
No thermal port— The block does not contain thermal ports.Show thermal port— The block contains multiple thermal conserving ports.
For more information about using thermal ports in actuator blocks, see Simulating Thermal Effects in Rotational and Translational Actuators.
Examples
Assumptions and Limitations
The block does not model the starting mechanism for a single-phase induction motor.
When you parameterize the block by motor ratings, the block derives the equivalent circuit model parameters by assuming that the effect of the magnetizing inductance Lm is negligible, and the magnetizing inductance is not included in the simulated component.
Ports
Output
Conserving
Parameters
References
[1] S.E. Lyshevski. Electromechanical Systems, Electric Machines, and Applied Mechatronics, CRC, 1999.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2008a


