Optimize
Optimize or solve equations in the Live Editor
Description
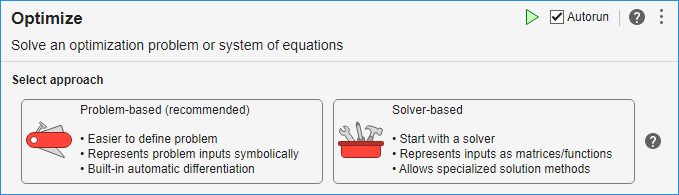
The Optimize task lets you choose between two ways to interactively optimize problems or to solve nonlinear systems of equations:
Problem-based (recommended) — Create symbolic optimization variables and expressions to represent the objective function and constraints or equations.
Solver-based — Represent the objective function and constraints or equations using standard MATLAB® code.
The task automatically generates MATLAB code for your live script.
Using the problem-based version of this task, you can:
Specify optimization variable arrays, including their bounds and initial values.
Specify the problem type: minimization, maximization, feasibility, or equation-solving.
Specify the objective and constraint functions, either by writing expressions or browsing for functions.
Optionally, choose a solver, and specify nondefault options.
Run the optimization.
Using the solver-based version of this task, you can:
Choose a solver based on the characteristics of your problem. If you have Global Optimization Toolbox, you can choose to use its solvers as well.
Specify the objective and constraint functions, either by writing functions or browsing for functions.
Specify solver options.
Run the optimization.
To get started using Optimize, see Get Started with Solver-Based Optimize Live Editor Task and Get Started with Problem-Based Optimize Live Editor Task. For suggestions on how to
use Optimize, see Use Solver-Based Optimize Live Editor Task Effectively or Use Problem-Based Optimize Live Editor Task Effectively. Currently, you cannot use
the fseminf, GlobalSearch, or
MultiStart solvers with
Optimize.
For general information about Live Editor tasks, see Add Interactive Tasks to a Live Script.
Open the Task
To add the Optimize task to a live script in the MATLAB Editor, on the Live Editor Insert tab, select Task > Optimize.
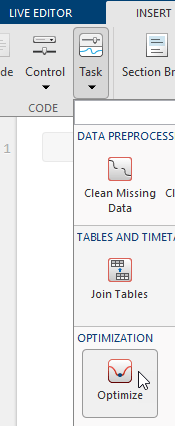
Alternatively, in a code block in the script, type a relevant keyword, such as
optim or fmincon. Select
Optimize from the suggested command completions.
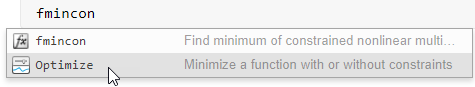
After you insert the task, select either Problem-based (recommended) or Solver-based.
Examples
- Get Started with Solver-Based Optimize Live Editor Task
- Get Started with Problem-Based Optimize Live Editor Task
- Constrained Nonlinear Problem Using Optimize Live Editor Task or Solver
- Feasibility Using Problem-Based Optimize Live Editor Task
- Optimize Live Editor Task with fmincon Solver
- Optimize Live Editor Task with lsqlin Solver
- Optimize Using the GPS Algorithm (Global Optimization Toolbox)
- Minimize Function with Many Local Minima (Global Optimization Toolbox)
- Pareto Front for Two Objectives (Global Optimization Toolbox)
- Use Problem-Based Optimize Live Editor Task Effectively
- Use Solver-Based Optimize Live Editor Task Effectively
- Solver-Based Optimization Problem Setup
- How to Use the Solver-Based Optimize Live Editor Task
- How to Use the Problem-Based Optimize Live Editor Task
Parameters
Limitations
Currently, Optimize has the following restrictions for multiobjective optimization.
You must specify your objective functions using a single function with multiple outputs. In other words, your objective function must output a vector of values, one entry for each objective.
All objective functions must use the same sense, minimization for the solver-based task, and either minimization or maximization for the problem-based task.
Tips
For functions with extra inputs, the solver-based and problem-based Optimize tasks have somewhat different requirements.
Solver-Based: Choose the optimization variable, and specify which workspace variables contain the fixed data inputs. For example, see Place Optimization Variables in One Vector and Data in Other Variables, which contains three function inputs:
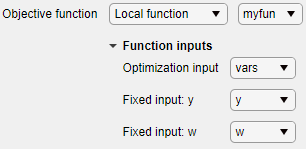
Optimize generates code only after you specify all function inputs.
Problem-Based: Specify an optimization variable or workspace variable name for each function input. If an input argument name in the function signature matches an existing optimization variable or workspace variable name, Optimize automatically selects that name.
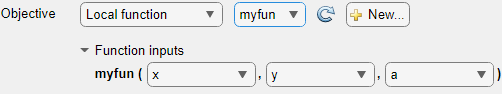
Optimize generates code only after you specify all function inputs.
Optimize cannot parse a function containing the
varargininput or a function that contains an error.If you select a function from a file, Optimize adds the file location to your MATLAB path.
If Optimize has a parsing error or if multiple local functions have the same name, the list of available local functions is empty.
Version History
Introduced in R2020bSee Also
Functions
fmincon|intlinprog|surrogateopt(Global Optimization Toolbox) |patternsearch(Global Optimization Toolbox)