mesh
Description
Examples
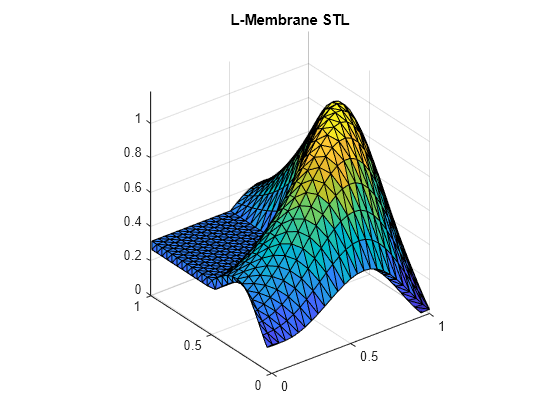
Read and plot the triangulation data from the L-membrane STL. You can use this to compare with the signed distance map.
triL = stlread("L-Membrane.stl"); trisurf(triL) title("L-Membrane STL") [az,el] = view; axis equal
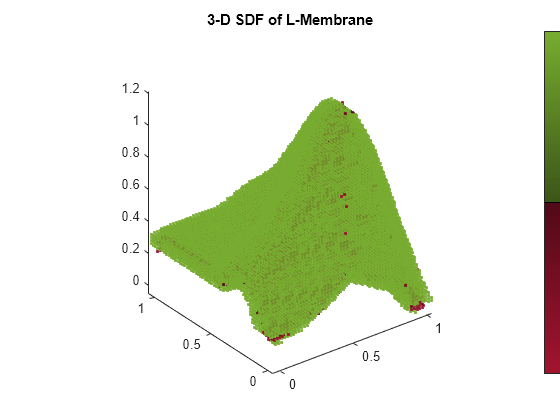
Create an empty 3-D signed distance field (SDF) and load the point cloud data for the L-membrane from a MAT file. The MAT file contains point cloud data and the sensor origin associated with each point cloud data.
sdm3D = signedDistanceMap3D(Resolution=50);
load LMembranePC.matInsert each point cloud into the signed distance field and show the updated 3-D SDF.
for i = 1:size(ptcloud,1) insertPointCloud(sdm3D,origin(i,:),ptcloud{i}); show(sdm3D,Colorbar="on"); view(az,el) axis equal drawnow pause(.25) end title(["3-D SDF of L-Membrane"])
Get all active voxels in the 3-D SDF.
vox = activeVoxels(sdm3D)
vox = struct with fields:
ID: 1
Centers: [49889×3 double]
Distances: [49889×1 double]
Sizes: [49889×1 double]
For demonstrative purposes, use a random xyz-offset from the voxel centers of the first three voxels as query points. Then get the distance and gradient using those query points.
querypts = vox.Centers(1:3,:) + 0.1*rand(3,3); d = distance(sdm3D,querypts)
d = 3×1
0.0379
-0.0447
0.0600
g = gradient(sdm3D,querypts)
g = 3×3
0.1924 1.5773 -1.4002
0.1689 1.6524 -0.8267
-0.0715 -0.2335 0.3677
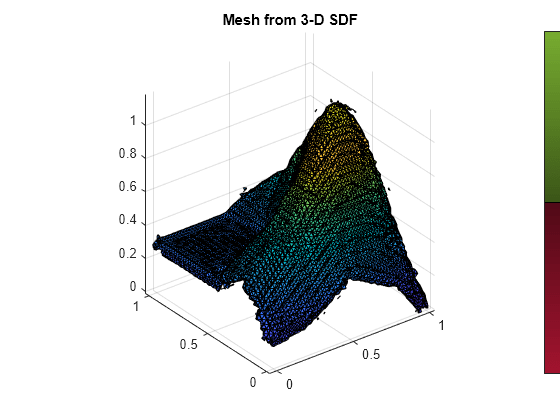
Generate a mesh from the 3-D signed distance field.
[vertices,faces] = mesh(sdm3D)
vertices = 18860×3
-0.0100 0.0068 0.1500
-0.0300 0.0059 0.1500
-0.0100 0.0100 0.1610
-0.0300 0.0100 0.1565
0.0100 0.0047 0.1500
-0.0100 -0.0100 0.1409
0.0100 -0.0100 0.1421
0.0100 0.0025 0.1700
-0.0010 0.0100 0.1700
0.0100 0.0094 0.1900
0.0089 0.0100 0.1900
0.0100 0.0100 0.1909
-0.0100 0.0187 0.1700
-0.0300 0.0259 0.1700
-0.0100 0.0552 0.1500
⋮
faces = 37094×3
2 1 3
4 2 3
7 1 6
5 1 7
9 3 1
9 1 8
8 1 5
8 10 11
9 8 11
10 12 11
3 14 4
13 14 3
15 16 17
16 18 17
9 13 3
⋮
Visualize the mesh data.
meshTri = triangulation(faces,vertices); trisurf(meshTri) axis equal title("Mesh from 3-D SDF")
If needed, you can use this mesh data to create a collision mesh using V-HACD. See collisionVHACD (Robotics System Toolbox) for more information.
Input Arguments
3-D signed distance map, specified as a signedDistanceMap3D object.
Output Arguments
Generated isosurface mesh vertices, returned as a V-by-3 matrix. Each row represents an xyz-position.
Generated isosurface mesh faces, returned as a F-by-3 matrix.
Each row is triangular face made from three vertices. Each element is an index
corresponding a vertex in the vertices argument.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2024b
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)