Grouped Statistics Calculations with Tall Arrays
This example shows how to calculate grouped statistics of a tall timetable containing power outage data. The example uses the grouptransform, groupsummary, and groupcounts functions to calculate various quantities of interest, such as the most common power outage cause in each region. Even though the raw data in this example only has about 1500 rows, you can use the techniques presented here on much larger data sets because no assumptions are made about the size of the data.
Create Datastore and Tall Timetable
The sample file, outages.csv, contains data representing electric utility outages in the United States. The file contains six columns: Region, OutageTime, Loss, Customers, RestorationTime, and Cause.
Create a datastore for the outages.csv file. Use the "TextScanFormats" option to specify the kind of data each column contains: categorical ("%C"), floating-point numeric ("%f"), or datetime ("%D").
data_formats = ["%C","%D","%f","%f","%D","%C"]; ds = tabularTextDatastore("outages.csv","TextscanFormats",data_formats);
Create a tall table on top of the datastore, and convert the tall table into a tall timetable. The OutageTime variable is used for the row times since it is the first datetime or duration variable in the table.
T = tall(ds); T = table2timetable(T)
T =
M×5 tall timetable
OutageTime Region Loss Customers RestorationTime Cause
__________ ______ ____ _________ _______________ _____
? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ?
: : : : : :
: : : : : :
Preview deferred. Learn more.
Replace Missing Data
Some of the rows in the RestorationTime variable have missing times, represented by NaT values. Remove these rows from the table.
T = rmmissing(T,"DataVariables","RestorationTime");
For the numeric variables in the timetable, instead of removing rows with missing values, replace the missing values with the mean value for each region.
T = grouptransform(T,"Region","meanfill",["Loss","Customers"]);
Use ismissing to confirm that no pieces of missing data remain in the table.
tf = any(ismissing(T),"all");
gather(tf)Evaluating tall expression using the Local MATLAB Session: - Pass 1 of 4: Completed in 0.21 sec - Pass 2 of 4: Completed in 0.41 sec - Pass 3 of 4: Completed in 0.36 sec - Pass 4 of 4: Completed in 0.34 sec Evaluation completed in 2.1 sec
ans = logical
0
Preview Data
Now that the data does not contain missing values, bring a small number of rows into memory to get an idea of what the data contains.
gather(head(T))
Evaluating tall expression using the Local MATLAB Session: - Pass 1 of 1: Completed in 0.2 sec Evaluation completed in 0.29 sec
ans=8×5 timetable
OutageTime Region Loss Customers RestorationTime Cause
________________ _________ ______ __________ ________________ _______________
2002-02-01 12:18 SouthWest 458.98 1.8202e+06 2002-02-07 16:50 winter storm
2003-02-07 21:15 SouthEast 289.4 1.4294e+05 2003-02-17 08:14 winter storm
2004-04-06 05:44 West 434.81 3.4037e+05 2004-04-06 06:10 equipment fault
2002-03-16 06:18 MidWest 186.44 2.1275e+05 2002-03-18 23:23 severe storm
2003-06-18 02:49 West 0 0 2003-06-18 10:54 attack
2004-06-20 14:39 West 231.29 1.5354e+05 2004-06-20 19:16 equipment fault
2002-06-06 19:28 West 311.86 1.5354e+05 2002-06-07 00:51 equipment fault
2003-07-16 16:23 NorthEast 239.93 49434 2003-07-17 01:12 fire
Mean Power Outage Duration by Region
Determine the mean power outage duration in each region using groupsummary. First, create a new variable OutageDuration in the table that contains the duration of each outage, found by subtracting the outage time from the restoration time. In the call to groupsummary, specify:
"Region"as the grouping variable"mean"as the computation method"OutageDuration"as the variable to operate on.
T.OutageDuration = T.RestorationTime - T.OutageTime; times = groupsummary(T,"Region","mean","OutageDuration")
times =
M×3 tall table
Region GroupCount mean_OutageDuration
______ __________ ___________________
? ? ?
? ? ?
? ? ?
: : :
: : :
Preview deferred. Learn more.
Change the display format of the duration results to be in days, and gather the results into memory. The results show the mean outage duration in each region, as well as the number of reported outages in each region.
times.mean_OutageDuration.Format = "d";
times = gather(times)Evaluating tall expression using the Local MATLAB Session: - Pass 1 of 2: Completed in 0.7 sec - Pass 2 of 2: Completed in 0.4 sec Evaluation completed in 1.5 sec
times=5×3 table
Region GroupCount mean_OutageDuration
_________ __________ ___________________
MidWest 138 34.135 days
NorthEast 548 24.21 days
SouthEast 379 1.7013 days
SouthWest 25 2.4799 days
West 349 28.061 days
Most Common Power Outage Causes by Region
Determine how often each power outage cause occurs in each region. Use groupcounts with the Cause and Region variables as grouping variables. Gather the results into memory.
causes = groupcounts(T,["Cause","Region"]); causes = gather(causes)
Evaluating tall expression using the Local MATLAB Session: - Pass 1 of 2: Completed in 0.21 sec - Pass 2 of 2: Completed in 0.17 sec Evaluation completed in 0.6 sec
causes=43×4 table
Cause Region GroupCount Percent
________________ _________ __________ ________
attack MidWest 12 0.83391
attack NorthEast 135 9.3815
attack SouthEast 19 1.3204
attack West 126 8.7561
earthquake NorthEast 1 0.069493
earthquake West 1 0.069493
energy emergency MidWest 19 1.3204
energy emergency NorthEast 29 2.0153
energy emergency SouthEast 79 5.4899
energy emergency SouthWest 7 0.48645
energy emergency West 46 3.1967
equipment fault MidWest 9 0.62543
equipment fault NorthEast 17 1.1814
equipment fault SouthEast 40 2.7797
equipment fault SouthWest 2 0.13899
equipment fault West 85 5.9069
⋮
Each cause occurs several times in the table, so even though the table contains the correct data it is not in the proper format to see how often each cause occurs in each region. To improve the presentation of the data, unstack the GroupCount variable so that each column corresponds to a region and each row corresponds to an outage cause.
RegionCauses = gather(unstack(causes,"GroupCount","Region","GroupingVariables","Cause"))
RegionCauses=10×6 table
Cause MidWest NorthEast SouthEast SouthWest West
________________ _______ _________ _________ _________ ____
attack 12 135 19 NaN 126
earthquake NaN 1 NaN NaN 1
energy emergency 19 29 79 7 46
equipment fault 9 17 40 2 85
fire NaN 5 3 NaN 17
severe storm 30 139 132 6 22
thunder storm 31 102 54 6 7
unknown 4 10 3 NaN 4
wind 16 40 13 3 22
winter storm 17 70 36 1 19
Not all combinations of outage causes and regions are represented in the data, so the resulting table contains some NaNs. Fill in the NaN values with zeros.
RegionCauses = fillmissing(RegionCauses,"constant",{"",0,0,0,0,0})
RegionCauses=10×6 table
Cause MidWest NorthEast SouthEast SouthWest West
________________ _______ _________ _________ _________ ____
attack 12 135 19 0 126
earthquake 0 1 0 0 1
energy emergency 19 29 79 7 46
equipment fault 9 17 40 2 85
fire 0 5 3 0 17
severe storm 30 139 132 6 22
thunder storm 31 102 54 6 7
unknown 4 10 3 0 4
wind 16 40 13 3 22
winter storm 17 70 36 1 19
Worst Power Outages in Each Region
Calculate the broadest customer impact for each power outage in each region.
WorstOutages = groupsummary(T,["Region","Cause"],"max","Customers"); WorstOutages = gather(WorstOutages)
Evaluating tall expression using the Local MATLAB Session: - Pass 1 of 2: Completed in 0.13 sec - Pass 2 of 2: Completed in 0.13 sec Evaluation completed in 0.39 sec
WorstOutages=43×4 table
Region Cause GroupCount max_Customers
_________ ________________ __________ _____________
MidWest attack 12 2.4403e+05
MidWest energy emergency 19 5.0376e+05
MidWest equipment fault 9 2.4403e+05
MidWest severe storm 30 3.972e+06
MidWest thunder storm 31 3.8233e+05
MidWest unknown 4 3.0879e+06
MidWest wind 16 2.8666e+05
MidWest winter storm 17 7.7697e+05
NorthEast attack 135 1.5005e+05
NorthEast earthquake 1 0
NorthEast energy emergency 29 1.5005e+05
NorthEast equipment fault 17 1.667e+05
NorthEast fire 5 4.5139e+05
NorthEast severe storm 139 1.0735e+06
NorthEast thunder storm 102 5.9689e+06
NorthEast unknown 10 2.4983e+06
⋮
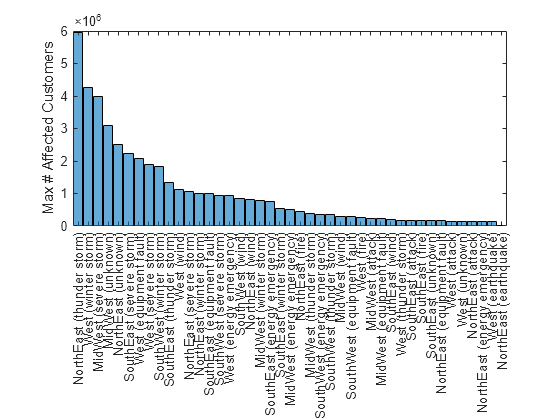
Combine the data in the Region and Cause variables into a single categorical variable by briefly converting them into strings. Then, create a categorical histogram of the maximum number of affected customers for each cause in each region.
WorstOutages.RegionCause = categorical(string(WorstOutages.Region)+" ("+string(WorstOutages.Cause)+")"); histogram("Categories",WorstOutages.RegionCause,"BinCounts",WorstOutages.max_Customers,... "DisplayOrder","descend") ylabel("Max # Affected Customers")
See Also
findgroups | splitapply | tall