imhistmatch
Adjust histogram of 2-D image to match histogram of reference image
Syntax
Description
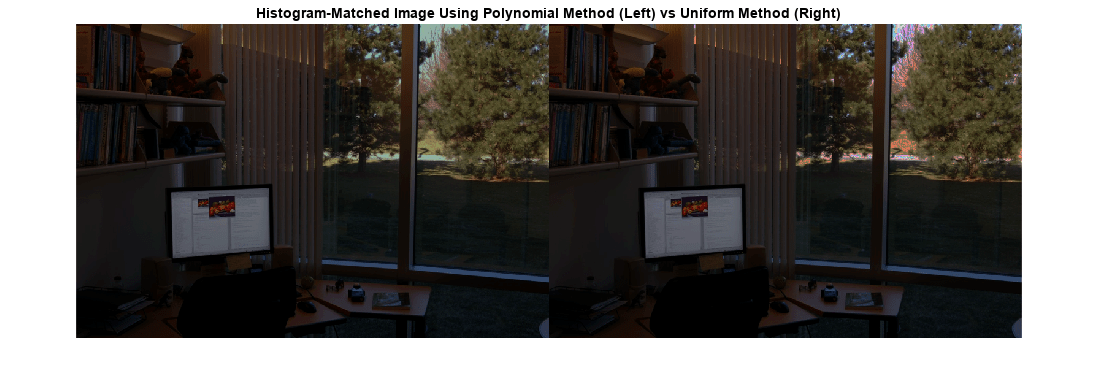
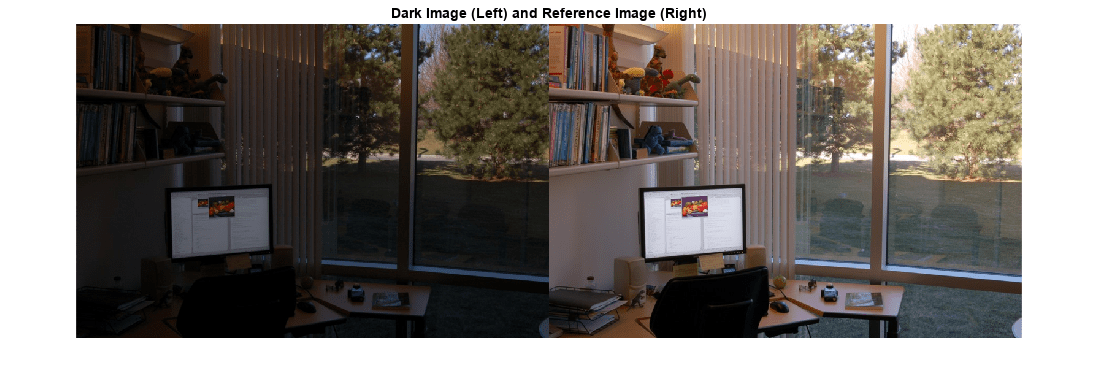
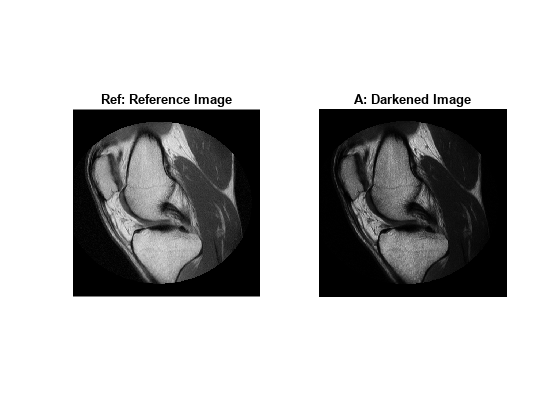
J = imhistmatch(I,ref)I such that the histogram approximately matches the
histogram of the reference image ref.
If both
Iandrefare RGB images, thenimhistmatchmatches each color channel ofIindependently to the corresponding color channel ofref.If
Iis an RGB image andrefis a grayscale image, thenimhistmatchmatches each channel ofIagainst the single histogram derived fromref.If
Iis a grayscale image, thenrefmust also be a grayscale image.
Images I and ref need not be equal in size.
J = imhistmatch(I,ref,nbins)nbins equally spaced bins within the appropriate range
for the given image data type. The returned image J has no
more than nbins discrete levels.
If the data type of the image is either
singleordouble, then the histogram range is [0, 1].If the data type of the image is
uint8, then the histogram range is [0, 255].If the data type of the image is
uint16, then the histogram range is [0, 65535].If the data type of the image is
int16, then the histogram range is [-32768, 32767].
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
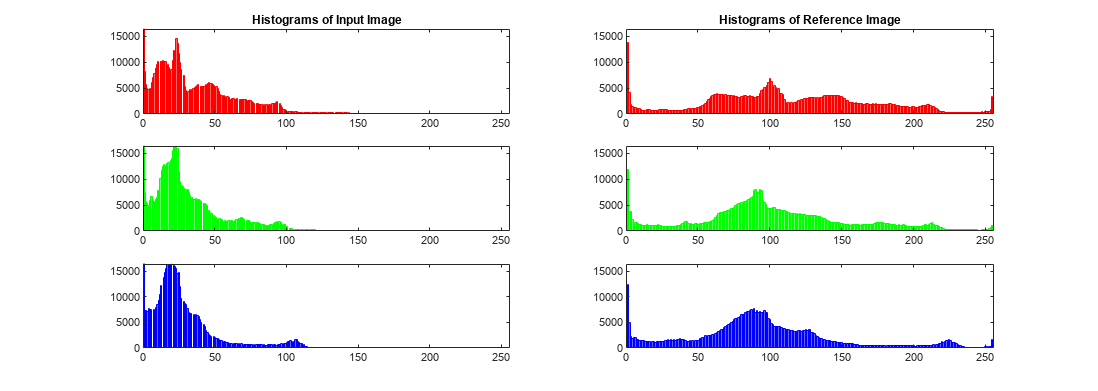
The objective of imhistmatch is to transform image I
such that the histogram of image J matches the histogram derived
from image ref. It consists of nbins equally
spaced bins which span the full range of the image data type. A consequence of matching
histograms in this way is that nbins also represents the upper
limit of the number of discrete data levels present in image
J.
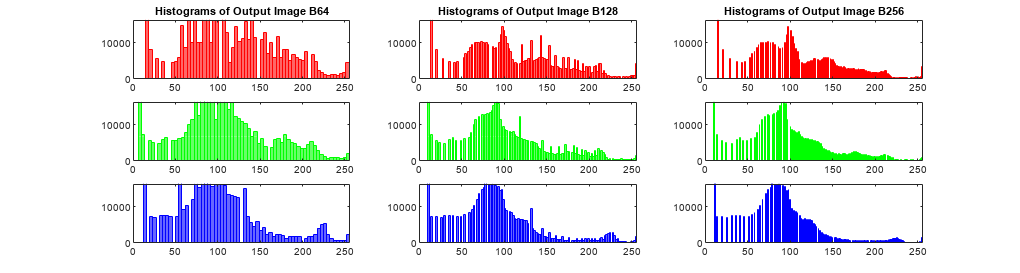
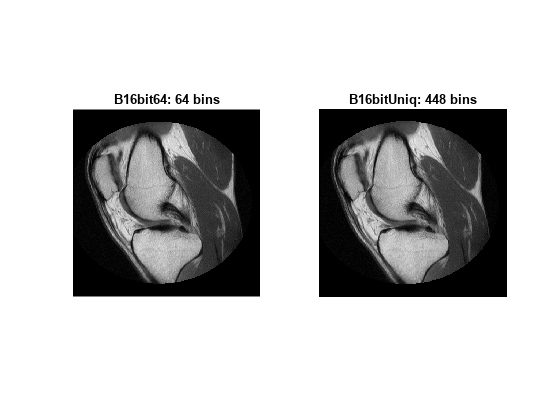
An important behavioral aspect of this algorithm to note is that as nbins
increases in value, the degree of rapid fluctuations between adjacent populated peaks in
the histogram of image J tends to increase. This can be seen in the
following histogram plots taken from the 16–bit grayscale MRI example.

An optimal value for nbins represents a
trade-off between more output levels (larger values of nbins)
while minimizing peak fluctuations in the histogram (smaller values
of nbins).
Version History
Introduced in R2012b