Needle Valve (IL)
Needle valve in an isothermal liquid system
Libraries:
Simscape /
Fluids /
Isothermal Liquid /
Valves & Orifices /
Flow Control Valves
Description
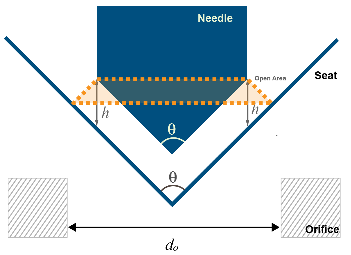
The Needle Valve (IL) block models flow reductions by a needle valve. The valve comprises a conical needle and a round, sharp-edged seat. The needle opens or closes according to the displacement signal at port S. A positive signal retracts the needle and opens the valve.
Opening Area
Needle Valve Schematic
Needle Valve Top View

The opening area of the valve is calculated as:
where:
h is the vertical distance between the outer edge of the needle and the seat, as indicated in the schematic above.
θ is the seat cone angle, which always matches the Needle cone angle.
d0 is the Seat orifice diameter.
Aleak is the Leakage area.
The opening area is bounded by the maximum displacement hmax:
For any needle displacement larger than hmax, Aopen is the sum of the maximum orifice area and the Leakage area:
For any combination of the signal at port S and the needle offset that is less than 0, the minimum valve area is the Leakage area.
If the Smoothing factor parameter is nonzero, the block smoothly
saturates the displacement between 0 and
hmax. For more information, see
Numerical Smoothing.
Mass Flow Rate Equation
Mass is conserved through the valve:
The mass flow rate through the valve is calculated as:
where:
Cd is the Discharge coefficient.
Avalve is the instantaneous valve open area.
Aport is the Cross-sectional area at ports A and B.
is the average fluid density.
Δp is the valve pressure difference pA – pB.
The critical pressure difference, Δpcrit, is the pressure differential associated with the Critical Reynolds number, Recrit, the flow regime transition point between laminar and turbulent flow:
Pressure loss describes the reduction of pressure in the valve due to a decrease in area. PRloss is calculated as:
Pressure recovery describes the positive pressure change in the valve due to an increase in area. If you do not want to capture this increase in pressure, clear the Pressure recovery check box. In this case, PRloss is 1.
Examples
Ports
Conserving
Input
Parameters
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2020a