Switches and Breakers
Use these blocks for protection in your electronic, mechatronic, or electrical power system.
Categories
- Switches and Breakers
Circuit breakers and multiple-port multiple-throw switches
- Relays
Single-port single- and double-throw relays
Featured Examples
Frequency-Dependent Transmission Line
A custom frequency-dependent transmission line model. The characteristic admittance and propagation function are first derived from the frequency-dependent resistance, reactance, and susceptance. The derived values are fitted using RF Toolbox. The Universal Line Model (ULM) [1] is then implemented in Simscape based on the fitted parameters. The results from the frequency-dependent transmission line model and the classic pi-section transmission line model are compared.
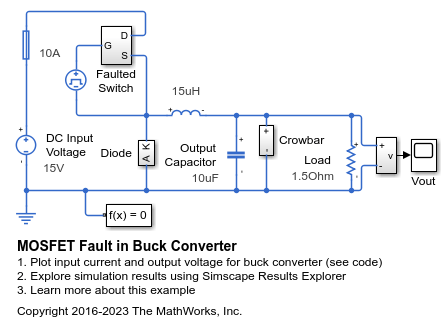
MOSFET Fault in Buck Converter
How a fault may be applied to a MOSFET in a power converter in order to explore the operation of protection circuitry. After the MOSFET becomes faulted, the crowbar circuitry is activated in order to clamp the output voltage across the load and eventually to cause the fuse to blow.
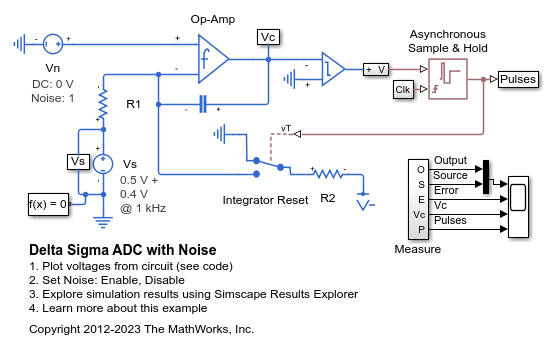
Delta Sigma ADC with Noise
A simple implementation of a sigma delta analog-to-digital converter. An input in the range 0 to Vref (=1V) is integrated until it causes the integrator to reset. The time to reset is proportional to the input value. Demodulation of the pulses is performed by a low-pass filter. The Asynchronous Sample & Hold block behaves like an edge-triggered D-type flip-flop, passing input U to output Y only on a rising edge of the clock. This model can be used to explore and understand the effect of op-amp impairments such as equivalent input noise on converter accuracy. To turn off the noise, open block Vn and select 'Disabled' for the noise mode.
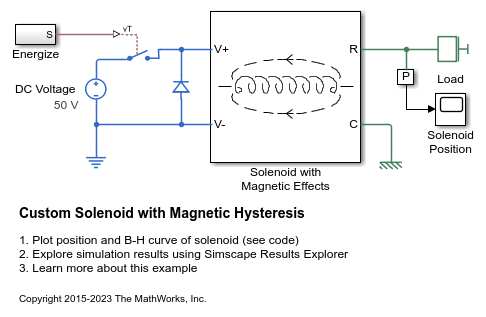
Custom Solenoid with Magnetic Hysteresis
A limited travel solenoid with return spring. Magnetic hysteresis is modeled using the Reluctance with Hysteresis library block.
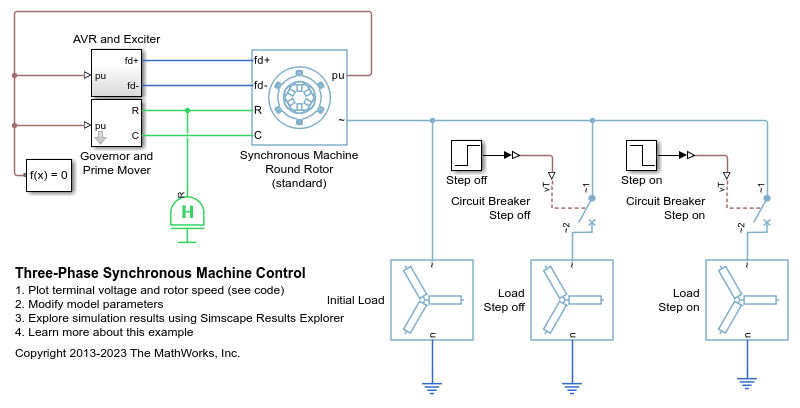
Three-Phase Synchronous Machine Control
Control and initialize a Synchronous Machine (SM). The test circuit shows the SM operating as a generator. The terminal voltage is controlled using an AVR and the speed is controlled using a governor.
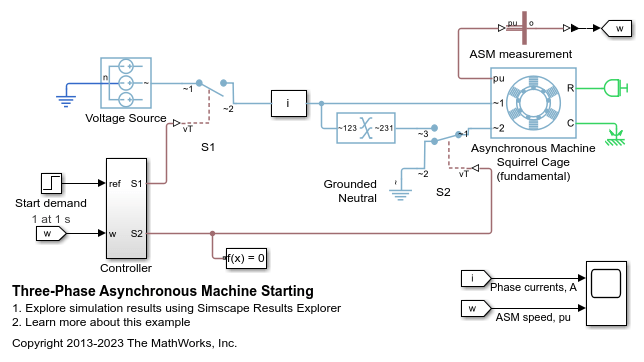
Three-Phase Asynchronous Machine Starting
Model a wye-delta starting circuit for an induction machine. When the supply is connected to the machine via switch S1, switch S2 is initially off resulting in the machine being connected in a wye configuration. Once the machine is close to synchronous speed, switch S2 is operated thereby reconnecting the machine in a delta configuration. The higher impedance seen by the supply when the motor is in wye configuration reduces the starting current, and causes less disruption to other connected loads.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)