Export Simulink Model to FMU with Variable Step Solver
This example demonstrates how to generate a Functional Mockup Unit (FMU) from a Simulink® model that uses a variable step solver. Export a Simulink model to an FMU that supports Co-Simulation in FMI version 2.0 or 3.0. Simulating an FMU with a variable step solver requires MATLAB® or MATLAB Runtime to be installed on the deployment machine.
Export Simulink Model to FMU
Open the Simulink model MechanicalSystemWithTranslationalFriction. This model uses daessc as the default variable step solver. For a detailed explanation of the model, see Mechanical System with Translational Friction.
openExample('simscape/MechanicalSystemWithTranslationalFrictionExample','SupportingFile', 'MechanicalSystemWithTranslationalFriction.slx') % save system, export to FMU with variable step solver requires model write permission save_system('MechanicalSystemWithTranslationalFriction', 'mechanical_system_local', 'OverwriteIfChangedOnDisk',true);
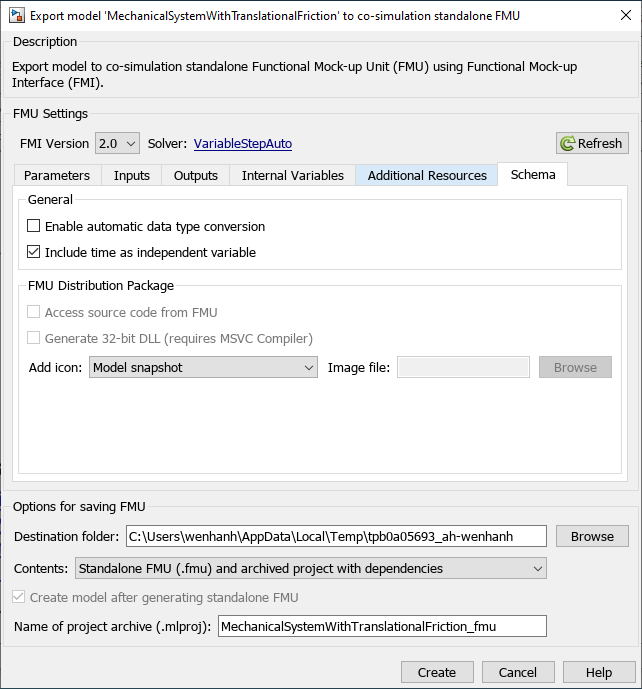
On the Simulation tab, click the drop-down button for Save. In the Export Model To section, click Standalone FMU. In the dialog box, configure the wrapper model and icon settings, and specify the save location for the generated FMU.
Configure the settings and click Create to export to the FMU. After creation of the FMU, the mechanical_system_local.fmu file can be found at the save location you specified in the Destination folder field of the dialog box.
Export Simulink Model to FMU via Command Line
Export this model to the FMU with the exportToFMU function.
% This function will generate the FMU and a harness model in the current directory. exportToFMU('mechanical_system_local', 'FMIVersion', '2.0', 'FMUType', 'CS', 'CreateModelAfterGeneratingFMU', 'on');
Simulate FMU with Variable Step Solver
Simulate FMU Within Simulink
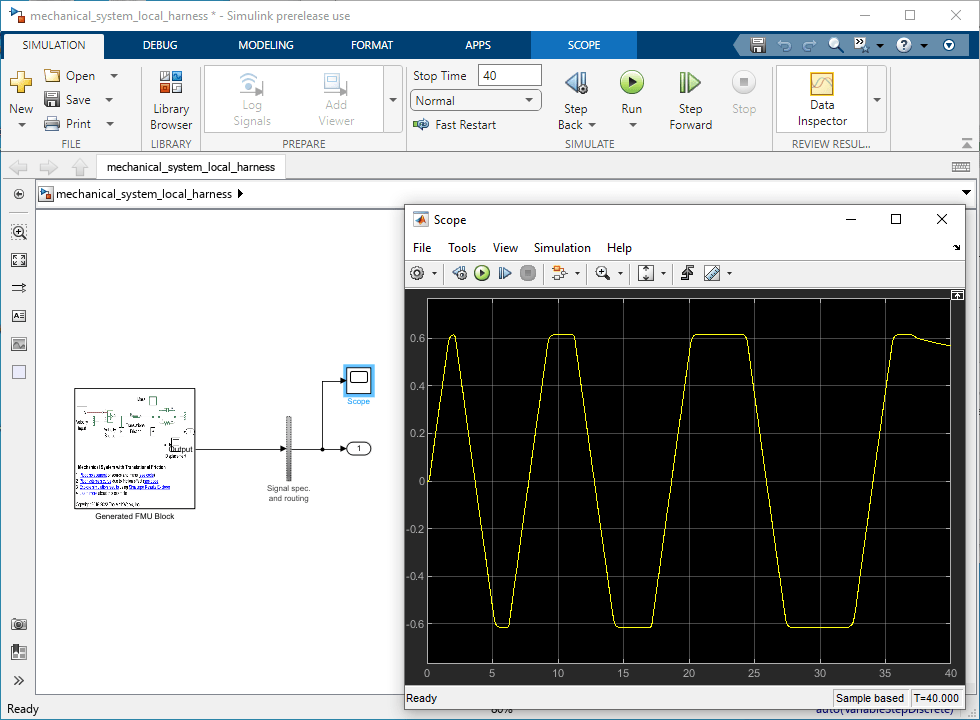
Open the harness model mechanical_system_local_harness and run the simulation. You can observe the result by adding a Scope block to the model.
open_system('mechanical_system_local_harness');
Simulate FMU with External Tools
To run the deployed FMU, you need an appropriate runtime environment. For more information, see Download and Install MATLAB Runtime (MATLAB Compiler SDK).
Use the compiler.runtime.download function to download MATLAB Runtime. Alternatively, use the link: https://www.mathworks.com/products/compiler/matlab-runtime.html.
The default MATLAB Runtime Installation Directory is:
Windows C:\Program Files\MATLAB\MATLAB Runtime\R2023b Linux /usr/local/MATLAB/MATLAB_Runtime/R2023b
After installation is complete, use these commands to set environment variables on the deployment machine:
Windows
set InstallationFolder='MATLAB runtime Path here'
set PATH=%PATH%;%InstallationFolder%\bin\win64;%InstallationFolder%\extern\bin\win64
% in linux shell terminal
export InstallationFolder='MATLAB runtime Path here'
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}:${InstallationFolder}/bin/glnxa64:${InstallationFolder}/extern/bin/glnxa64
% in linux csh terminal
setenv InstallationFolder 'MATLAB runtime Path here'
setenv LD_LIBRARY_PATH ${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}:${InstallationFolder}/bin/glnxa64:${InstallationFolder}/extern/bin/glnxa64
For more information, see Set MATLAB Runtime Path for Deployment.
MATLAB Runtime in Environment Variable
These steps use the FMU Compliance Checker to validate the generated FMU. For information about the FMU Compliance Checker, see FMI Compliance Checker Git repo.
To run the FMU with FMU Compliance Checker, open the Command Prompt and go to the location where FMU Compliance Checker is installed. Set environment variable with the command illustrated in the previous section.
Run the FMU with this command and observe the output in the terminal.
% on windows FMUCheck.win64 mechanical_system.fmu % on linux ./FMUCheck.linux64 mechanical_system.fmu
