Manage Multiple Build and Verification Workflows Using Processes
With the CI Support Package for Simulink, you can define a development and verification process for your team by using a process model. Inside your process model, you can define multiple processes for the different build and verification workflows, environments, and other situations that your team needs a defined process for. A process is a group of tasks or subprocesses inside your process model. For example, you can create separate processes for:
Smoke testing with fail-fast tasks
Local prequalification
CI builds
Different stages of the development process
Different product readiness levels
Processes allow you to have multiple build and verification processes standardized and
available to your team, with the tasks configured appropriately for that specific
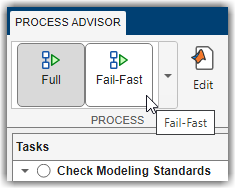
workflow. In Process Advisor, you can select which process you want to use
from the Process gallery in the toolstrip. APIs like the
runprocess function also allow you to specify which
Process to run.
Open Process Model
You can create multiple processes by editing the process model file for your project. If you do not have a project or process model, see Automate and Run Tasks with Process Advisor to get started.
Open the project that contains your files.
Open Process Advisor. On the Project tab, in the Tools section, click Process Advisor.
Edit the process model by clicking the Edit button
 in the toolstrip.
in the toolstrip.
Overview of Processes
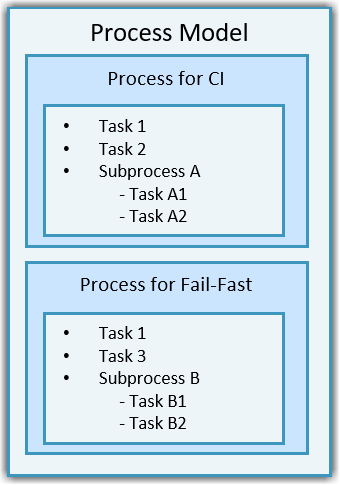
Your process model can contain multiple processes and each process can contain tasks and subprocesses. For example, you can have one process for your full qualification process and another process for fail-fast, local prequalification. Each of those processes can contain tasks and or subprocesses of tasks. Additionally, you can share tasks and subprocesses across multiple processes. You can use the padv.Process methods like addTask, addSubprocess, addDependsOnRelationship, and addRunsAfterRelationship inside the process model to define the tasks, subprocesses, and relationships for your process.
Define New Processes
Add Processes
To add a new process inside your process model, use the method addProcess.
function processmodel(pm) arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end % Add processes processA = pm.addProcess("A"); processB = pm.addProcess("B"); end
Define Processes Using Process-Specific Methods
When you define multiple processes inside your process model, use the padv.Process methods to add tasks, subprocesses, and relationships directly to your process. Unlike the methods for padv.ProcessModel, which add tasks and subprocesses to the default process inside your process model, the padv.Process methods allow you to specify which specific process you want to add a task, subprocess, or relationship to. For example, if you have multiple processes and want to specify a dependency between two tasks inside a process, use the padv.Process method addDependsOnRelationship to specify that dependency. The method addDependsOnRelationship accepts the process name as an input argument. Using process-specific methods is especially important if you share tasks across multiple processes and need to define different relationships to that task within each process.
The class padv.Process has several methods that you can use to customize the process. For more information, see padv.Process.
addTask | Add task to process myProcess.addTask("myTask"); |
addSubprocess | Add subprocess to process myProcess.addSubprocess("mySubprocess"); |
addDependsOnRelationship | Create dependency between two tasks myProcess.addDependsOnRelationship(... Source=taskB,... Dependency=taskA); Dependency task before the Source task. |
addRunsAfterRelationship | Specify predecessor for task myProcess.addRunsAfterRelationship(... Source=taskB,... Predecessor=taskA); Predecessor task before the Source task when possible. |
Add Tasks and Organize Tasks Within Process. You can add tasks directly to a specific process by using the addTask method
for padv.Process. You can also use subprocesses to organize
tasks within your process. For example, this process model uses the
padv.Process methods to add example tasks and
subprocesses to specific processes in the process model.
function processmodel(pm) % This function defines a process model for a project by setting up processes, % subprocesses, and tasks within those processes. arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end % --- Processes --- % Add processes processA = pm.addProcess("A"); processB = pm.addProcess("B"); % --- Tasks --- % Create example tasks task1 = padv.Task("task1"); task2 = padv.Task("task2"); task3 = padv.Task("task3"); taskA1 = padv.Task("taskA1"); taskA2 = padv.Task("taskA2"); taskB1 = padv.Task("taskB1"); taskB2 = padv.Task("taskB2"); % --- Subprocesses --- % Add subprocesses to parent process subprocessA = processA.addSubprocess("subprocessA"); % Add to process A subprocessB = processB.addSubprocess("subprocessB"); % Add to process B % --- Add Tasks to Processes --- processA.addTask(task1); % Add task1 to process A processA.addTask(task2); % Add task2 to process A processB.addTask(task1); % Reuse task1 in process B processB.addTask(task3); % Add task3 to process B % --- Add Tasks to Subprocesses --- subprocessA.addTask(taskA1); % Add taskA1 to subprocessA under process A subprocessA.addTask(taskA2); % Add taskA2 to subprocessA under process A subprocessB.addTask(taskB1); % Add taskB1 to subprocessB under process B subprocessB.addTask(taskB2); % Add taskB2 to subprocessB under process B end
Note
By default, if you do not add processes to a process model, the
process model automatically creates a default process,
"CIPipeline", for you. If you add tasks and
subprocesses directly to the padv.ProcessModel
object, you are actually adding those tasks and subprocesses to an
intermediate, default process. By default, the default process is
"CIPipeline".
You can access the padv.Process object that
represents the default process by using the method
findProcess inside the process model.
function processmodel(pm) % Defines the project's processmodel arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end pm.addTask("MyCustomTask"); processCI = pm.findProcess("CIPipeline"); end
Add Task Relationships to Process. To specify a preferred task execution order inside a specific process, use the padv.Process method addRunsAfterRelationship. For example, for each process, you can specify that a shared task, task1, should run after a specific task in that process.
% Create Dependencies Within Specific Process processA.addRunsAfterRelationship(Source = task2,... Predecessor = task1); processB.addRunsAfterRelationship(Source = task3,... Predecessor = task1);
You can add a dependency between tasks inside a specific process by using the padv.Process method addDependsOnRelationship. For example, you can specify that for processA, task2 depends on task1 and cannot run without task1 running first.
% Add dependency between tasks inside Process A processA.addDependsOnRelationship(... Source = task2,... Dependency = task1);
Example Process Model with Multiple Processes
Suppose that you have two Model Advisor configuration files:
allChecks.json— Contains all of the Model Advisor checks that you want to runquickChecks.json— Contains a subset of your Model Advisor checks for fast-fail checking
For your full process, you can add an instance of the
RunModelStandards task that runs using
allChecks.json. For your "fail-fast" process, you can add
an instance of the RunModelStandards task that runs using
quickChecks.json. Note that this code shares the query
object, findModels, across the tasks to improve
performance. By sharing the query object, the
build system can avoid re-running the
padv.builtin.query.FindModels query. For more information,
see Best Practices for Process Model Authoring.
function processmodel(pm) % Defines the project's processmodel arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end fullProcess = pm.addProcess("Full"); failfastProcess = pm.addProcess("Fail-Fast"); % Define Shared Query and Add Shared Query to Process Model findModels = padv.builtin.query.FindModels(Name="ModelsQuery"); pm.addQuery(findModels); % Add Full Model Advisor Checks Task to CI Process % (uses allChecks.json MA config file) taskFullMA = fullProcess.addTask(... padv.builtin.task.RunModelStandards(... Name = "fullMATask",... IterationQuery=findModels)); taskFullMA.addInputQueries(... padv.builtin.query.FindFileWithAddress(... Type='ma_config_file', Path=fullfile('tools','allChecks.json'))); % Add Quick Checks Task to Fail-Fast Processs % (uses quickChecks.json MA config file) taskFailFastMA = failfastProcess.addTask(... padv.builtin.task.RunModelStandards(... Name = "quickChecksTask",... IterationQuery=findModels)); taskFailFastMA.Title = "Check Modeling Standards (subset)"; taskFailFastMA.addInputQueries(... padv.builtin.query.FindFileWithAddress(... Type='ma_config_file', Path=fullfile('tools','quickChecks.json'))); end
Use Specific Process
In Process Advisor, you can select which process you want to use from the Process gallery in the toolstrip. By default, processes appear in the order that you define them in the process model.

APIs like the runprocess, processadvisor, and padv.pipeline.generatePipeline functions also allow you to specify which process to use.
runprocess(Process = "Fail-Fast") processadvisor("AHRS_Voter","Fail-Fast") options = padv.pipeline.GitLabOptions; padv.pipeline.generatePipeline(options,"Full");
Default Process Behavior
By default, the default process is the first process that you add to your process model. When you open Process Advisor for the first time, the Tasks column shows the tasks in your default process. APIs like the runprocess function use the default process unless you specify which process to use. You can specify a different default process by overriding the DefaultProcessId property of the padv.ProcessModel object inside your process model.
pm.DefaultProcessId = "Fail-Fast";To identify which process is the default process for the process model, you can use the getprocess function in the MATLAB® Command Window.
getprocess().DefaultProcessId
The first time that you open Process Advisor, the app opens to the default process. Otherwise, Process Advisor re-opens your last opened process. To force the next Process Advisor session to open the default process instead of the last opened process, you can reset your user settings from the MATLAB Command Window.
us = padv.UserSettings.get(); us.resetToDefaultValues();
See Also
padv.Process | padv.Subprocess