Considerations and Limitations for startup Variant Activation
Time
Combining startup and code compile Variant Activation Times in Variant Conditions
Simulink® does not support combining variant conditions with startup
and code compile variant activation times in a model.
Case 1: Variant Source Block with startup Activation Time Connected to a Variant Source Block with code compile Activation Time
Consider a model with two Variant Source blocks,
VS_CC and VS_ST, with the Variant
activation time parameter set to code compile and
startup, respectively.
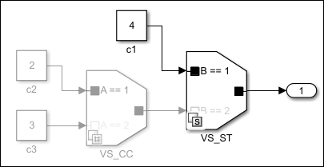
During model compilation, the VS_ST block propagates the variant
condition, B==2 to the VS_CC block. So, the
propagated variant condition on the VS_CC block is (A == 1
&& B == 2) || (A == 2 && B == 2), which combines conditions
with startup and code compile activation times. This
combination results in a compilation error.
Case 2: Variant Source Block with startup Activation Time Connected to a Variant Subsystem Block with code compile Activation Time
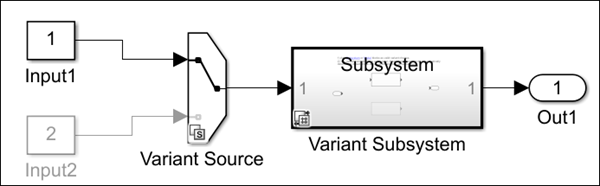
In this model, a Variant Source block with the Variant
activation time parameter set to startup is connected to a
Variant Subsystem block with the Variant activation
time parameter set to code compile. The
Propagate conditions outside of variant subsystem and the
Built-in empty choice parameters on the Variant
Subsystem block are set to on. These settings result in
propagation of conditions that combines startup and code
compile activation times and produces a compilation error.
Note
This constraint is applicable to any Simulink block that supports variant condition propagation. For example, you cannot
combine startup variant conditions with Simulink
Function blocks or Initialize, Reset, and
Terminate blocks that have the Generate preprocessor
conditionals parameter set to on. This parameter works
similarly to the code compile variant activation time. For
information on condition propagation with different blocks, see Propagate Variant Conditions from Variant Blocks Upstream and Downstream.
The compilation error for this scenario normally indicates the block that caused the
error. If the error message does not indicate the block, then the variant condition that
combined startup and code compile activation times
could have propagated to a hidden block that Simulink inserted for internal use. Such blocks are not visible in the
model.
Exception Scenarios That Support Combining Variant Conditions with startup and code compile Variant Activation Times
These modeling scenarios support combining variant conditions with
startup and code compile activation times:
Simulink Function blocks that inherit variant conditions from Function Caller blocks in a model. The variant condition assigned to the Simulink Function block is a logical OR of the variant conditions propagated to the Function Caller blocks. In such cases, the Function Caller blocks can have
startupandcode compileactivation times.Data Store Memory blocks in a model. These blocks receive a logical OR of the variant conditions propagated to the corresponding Data Store Read and Data Store Write blocks in the model. The reader and writer blocks in such models can have
startupandcode compileactivation times.
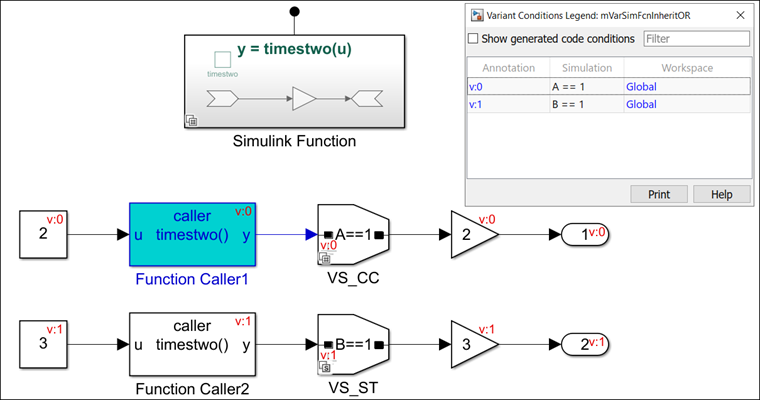
In this model, the Variant control parameter on the function-call
port block in the Simulink Function block is set to
(inherit). The Function Caller blocks,
Function Caller A and Function Caller B, receive
variant conditions with code compile and startup
activation times from the connected Variant Source blocks. The
Simulink Function block inherits a combination of these variant
conditions. This case does not result in a compilation error.
Use of Variant Control Variables with startup Variant Activation Time in Another Variant Block
You cannot use a variant control variable used in a block with
startup activation time in another variant block with a different
activation time.
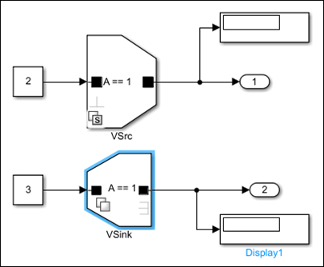
Consider a model with two variant blocks, VSrc and
VSink, with the Variant activation time parameter
set to startup and update diagram, respectively. Both
the blocks use the same variant control variable, A. This results in a
compile-time error.