Convert RGB Image to Grayscale by Using a Pixel Processing Subsystem Block
This example shows how to convert an RGB image to grayscale by using a Pixel Processing Subsystem block. Converting images to grayscale is an important step in image processing tasks such as corner detection. This example implements grayscale conversion using both the mean and luminosity methods, which weigh the red, green, and blue color channels differently. The luminosity method accounts for the different sensitivities that human eyes have for these colors and the mean method does not.
Inspect Model
1. Open the model.
model = 'RGBToGrayscalePixelProcessing';
open_system(model);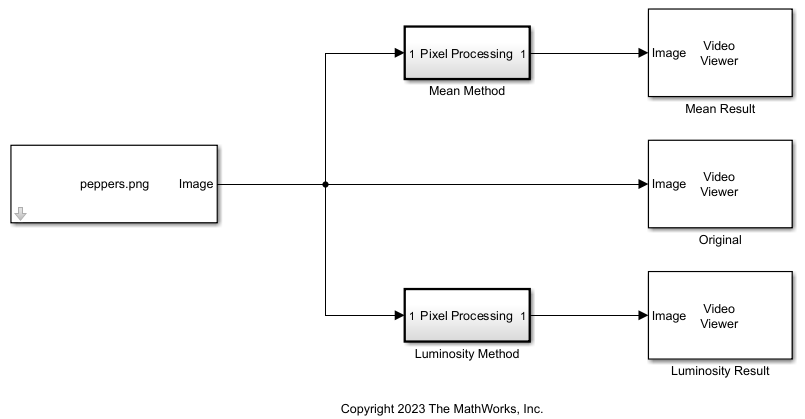
The model imports an image by using an Image From File block from Computer Vision Toolbox™. The model uses two Pixel Processing Subsystem blocks to convert the image to grayscale in two different ways. Each Pixel Processing Subsystem block iterates over each pixel in the input image. At each iteration step, each Pixel Processing Subsystem block receives a 1-by-1-by-3 matrix, called the neighborhood, that contains the three color channel values for a pixel. The Pixel Processing Subsystem blocks in the model contain two different algorithms that each derive a brightness from the neighborhood.
The model displays the original image and each output image by using Video Viewer blocks from Computer Vision Toolbox.
2. Open the MeanMethod subsystem.
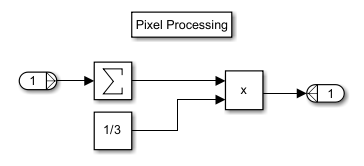
The subsystem uses a Sum of Elements block to add the three channel values together, then multiplies the sum by 1/3 to calculate the mean brightness value of the pixel.
3. Open the Luminosity Method subsystem.
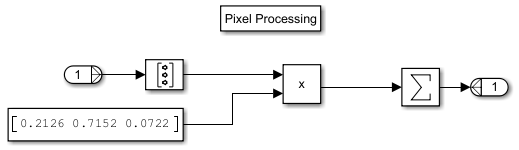
The subsystem calculates a weighted mean to account for the different sensitivities human eyes have for red, blue, and green light by:
Converting the 1-by-1-by-3 neighborhood to a 3-by-1 column vector by using a Reshape block
Multiplying the 3-by-1 column vector by the row vector
[0.2126 0.7152 0.0722]Passing the product through a Sum of Elements block
Simulate Model and View Results
Simulate the model.
sim(model);
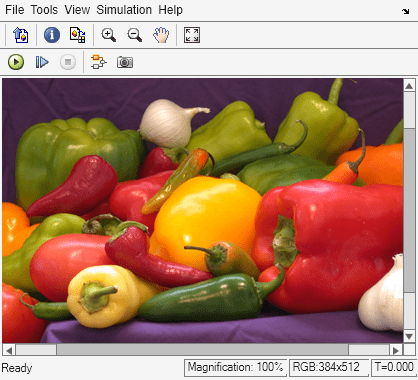
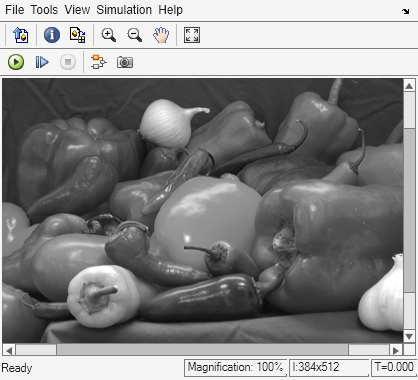
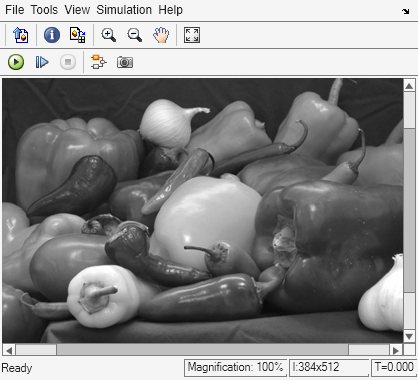
Each Pixel Processing Subsystem block produces a single-channel grayscale version of the three-channel RGB input image.