Work with Velodyne ROS Messages
This example shows how to handle VelodyneScan messages from a Velodyne LiDAR.
Velodyne ROS messages store data in a format that requires some interpretation before it can be used for further processing. MATLAB® can help you by formatting Velodyne ROS messages for easy use.
Prerequisites: Work with Basic ROS Messages
Load Sample Messages
Load sample Velodyne messages. These messages are populated with data gathered from Velodyne LiDAR sensor.
load("lidarData_ConstructionRoad.mat")VelodyneScan Messages
VelodyneScan messages are ROS messages that contain Velodyne LIDAR scan packets. You can see the standard ROS format for a VelodyneScan message by creating an empty message of the appropriate type. Use messages in structure format for better performance.
emptyveloScan = rosmessage("velodyne_msgs/VelodyneScan","DataFormat","struct")
emptyveloScan = struct with fields:
MessageType: 'velodyne_msgs/VelodyneScan'
Header: [1×1 struct]
Packets: [0×1 struct]
Since you created an empty message, emptyveloScan does not contain any meaningful data. For convenience, the loaded lidarData_ConstructionRoad.mat file contains a set of VelodyneScan messages that are fully populated and stored in the msgs variable. Each element in the msgs cell array is a VelodyneScan ROS message struct. The primary data in each VelodyneScan message is in the Packets property, it contains multiple VelodynePacket messages. You can see the standard ROS format for a VelodynePacket message by creating an empty message of the appropriate type.
emptyveloPkt = rosmessage("velodyne_msgs/VelodynePacket","DataFormat","struct")
emptyveloPkt = struct with fields:
MessageType: 'velodyne_msgs/VelodynePacket'
Stamp: [1×1 struct]
Data: [1206×1 uint8]
Create Velodyne ROS Message Reader
The velodyneROSMessageReader object reads point cloud data from VelodyneScan ROS messages based on their specified model type. Note that providing an incorrect device model may result in improperly calibrated point clouds. This example uses messages from the "HDL32E" model.
veloReader = velodyneROSMessageReader(msgs,"HDL32E")veloReader =
velodyneROSMessageReader with properties:
VelodyneMessages: {28×1 cell}
DeviceModel: 'HDL32E'
CalibrationFile: 'M:\jobarchive\Bdoc21b\2021_06_16_h16m50s15_job1697727_pass\matlab\toolbox\shared\pointclouds\utilities\velodyneFileReaderConfiguration\HDL32E.xml'
NumberOfFrames: 55
Duration: 2.7477 sec
StartTime: 1145.2 sec
EndTime: 1147.9 sec
Timestamps: [1145.2 sec 1145.2 sec 1145.3 sec 1145.3 sec 1145.4 sec 1145.4 sec 1145.5 sec 1145.5 sec 1145.6 sec 1145.6 sec 1145.7 sec 1145.7 sec 1145.8 sec 1145.8 sec 1145.9 sec 1145.9 sec … ]
CurrentTime: 1145.2 sec
Extract Point Clouds
You can extract point clouds from the raw packets message with the help of this velodyneROSMessageReader object. By providing a specific frame number or timestamp, one point cloud can be extracted from velodyneROSMessageReader object using the readFrame object function. If you call readFrame without a frame number or timestamp, it extracts the next point cloud in the sequence based on the CurrentTime property.
Create a duration scalar that represents one second after the first point cloud reading.
timeDuration = veloReader.StartTime + seconds(1);
Read the first point cloud recorded at or after the given time duration.
ptCloudObj = readFrame(veloReader,timeDuration);
Access Location data in the point cloud.
ptCloudLoc = ptCloudObj.Location;
Reset the CurrentTime property of veloReader to the default value
reset(veloReader)
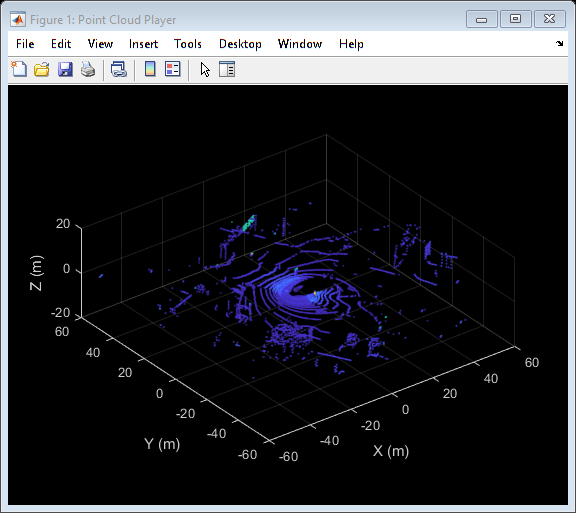
Display All Point Clouds
You can also loop through all point clouds in the input Velodyne ROS messages.
Define x-, y-, and z-axes limits for pcplayer in meters. Label the axes.
xlimits = [-60 60]; ylimits = [-60 60]; zlimits = [-20 20];
Create the point cloud player.
player = pcplayer(xlimits,ylimits,zlimits);
Label the axes.
xlabel(player.Axes,"X (m)"); ylabel(player.Axes,"Y (m)"); zlabel(player.Axes,"Z (m)");
The first point cloud of interest is captured at 0.3 second into the input messages. Set the CurrentTime property to that time to begin reading point clouds from there.
veloReader.CurrentTime = veloReader.StartTime + seconds(0.3);
Display the point cloud stream for 2 seconds. To check if a new frame is available and continue past 2 seconds, remove the last while condition. Iterate through the file by calling readFrame to read in point clouds. Display them using the point cloud player.
while(hasFrame(veloReader) && isOpen(player) && (veloReader.CurrentTime < veloReader.StartTime + seconds(2))) ptCloudObj = readFrame(veloReader); view(player,ptCloudObj.Location,ptCloudObj.Intensity); pause(0.1); end
See Also
rosmessage | velodyneROSMessageReader