Use BeagleBone Black Serial Port to Connect to Device
This example shows how to create a connection to a serial device, write data to the device, and read data from the device.
Caution
Excessive voltage and current can damage the BeagleBone® Black hardware. Observe the manufacturer precautions for handling the
BeagleBone Black hardware and connecting it to other devices. For more information, see
the local copy of the BeagleBone drivers and documentation in the BeagleBone Black Getting
Started folder on your host computer, or Getting Started with BeagleBone
Black.
Create a connection to the BeagleBone Black hardware.
bbb = beaglebone;
Show the location of the Tx and Rx pins on the GPIO header.
showAllPins(bbb)
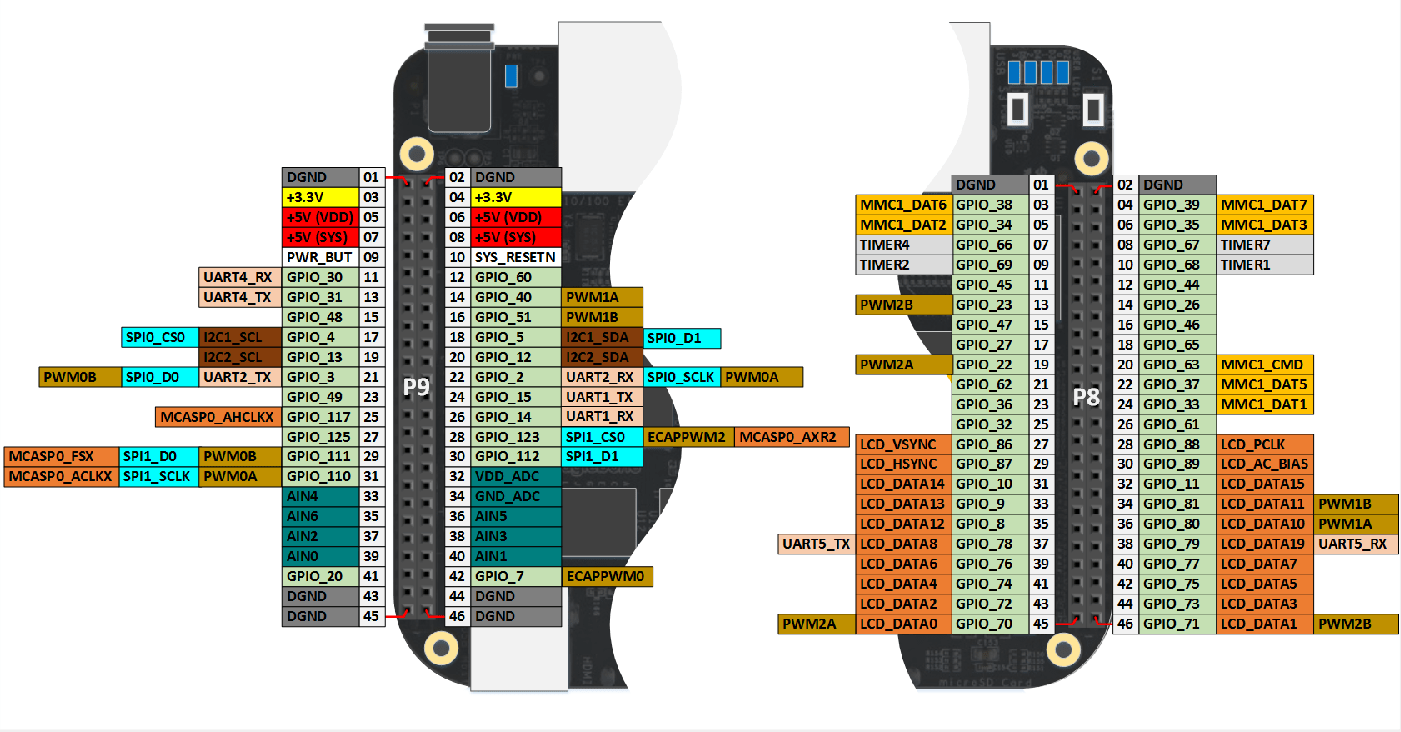
Connect the BeagleBone Black hardware to a
+3.3Vserial device.BeagleBone Black hardware uses
+3.3V. Do not connect BeagleBone Black hardware directly to devices that use higher voltages.To receive data, connect the
P9_26 (UART1_RXD)pin on the BeagleBone Black hardware to the TxD pin on the serial device.To transmit data, connect the
P9_24 (UART1_TXD)pin on the BeagleBone Black hardware to the RxD pin on the serial device.Connect a ground pin,
GND, on the BeagleBone Black hardware to theGNDpin on the serial device.Connect a
+3.3Vpin on the BeagleBone Black hardware to theVCCpin on the serial device.
Restart the BeagleBone Black hardware. After the hardware restarts, you can use
serialdevto exchange data with serial devices.Before continuing, research the manufacturer product information to determine which baud rate, data bits, parity, and stop bit settings the serial device supports.
Use
enableSerialPortto reconfigure GPIO pinsP9_26andP9_24asUART1_RXDandUART1_TXD.enableSerialPort(bbb, 1) bbb.AvailableSerialPorts
ans = '/dev/ttyO1'In
'/dev/ttyO1', the'O'is the capital letterO, not the number zero.Use
serialdevto create a connection to the serial device and assign the connection to an object.serial = beaglebone.serialdev(bbb,'/dev/ttyO1')serial = serialdev with properties: BaudRate: 115200 DataBits: 8 Parity: 'none' StopBits: 1 Timeout: 10In this example, the connection uses the default values for baud rate (
115200), data bits (8), parity ('none'), and stop bit (1).If the serial device requires nondefault values, use a set of optional arguments to override those defaults.
serial = beaglebone.serialdev(bbb,'/dev/ttyO1',115200,8,'none',2)
serialdev with properties: Port: '/dev/ttyO1' BaudRate: 115200 DataBits: 8 Parity: 'none' StopBits: 1 Timeout: 10This example overrides the default value of
StopBitsby setting it to2. The other arguments maintain the correct sequence of arguments to the left of the rightmost overriding value.You can write values to the serial device.
write(serial,[10 12],'uint16')In this example, you write two values to the serial device. The values override the default precision,
uint8, by setting it touint16.You can also read an array of values from the serial port.
output = read(serial,100)
This example reads a 100-element array of
uint8values from the serial device.If the serial connection times out during read operations, you can adjust the time out period by assigning a new value to the
Timeoutproperty.serial.Timeout = 20
serialdev with properties: Port: '/dev/ttyO1' BaudRate: 115200 DataBits: 8 Parity: 'none' StopBits: 1 Timeout: 20
When you are finished using the serial interface, restart the hardware to make additional GPIO pins available.