Apply Multiple Filters to Integral Image
This example shows how to apply multiple box filters of varying sizes to an image using integral image filtering. Integral image is a useful image representation from which local image sums can be computed rapidly. A box filter can be thought of as a local weighted sum at each pixel.
Read an image into the workspace and display it.
originalImage = imread('cameraman.tif'); figure imshow(originalImage) title('Original Image')

Define the sizes of the three box filters.
filterSizes = [7 7;11 11;15 15];
Pad the image to accommodate the size of the largest box filter. Pad each dimension by an amount equal to half the size of the largest filter. Note the use of replicate-style padding to help reduce boundary artifacts.
maxFilterSize = max(filterSizes); padSize = (maxFilterSize - 1)/2; paddedImage = padarray(originalImage,padSize,'replicate','both');
Compute the integral image representation of the padded image using the integralImage function and display it. The integral image is monotonically non-decreasing from left to right and top to bottom. Each pixel represents the sum of all pixel intensities to the top and left of the current pixel in the image.
intImage = integralImage(paddedImage);
figure
imshow(intImage,[])
title('Integral Image Representation')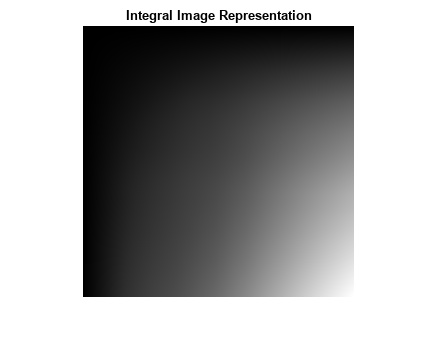
Apply three box filters of varying sizes to the integral image. The integralBoxFilter function can be used to apply a 2-D box filter to the integral image representation of an image.
filteredImage1 = integralBoxFilter(intImage, filterSizes(1,:)); filteredImage2 = integralBoxFilter(intImage, filterSizes(2,:)); filteredImage3 = integralBoxFilter(intImage, filterSizes(3,:));
The integralBoxFilter function returns only parts of the filtering that are computed without padding. Filtering the same integral image with different sized box filters results in different sized outputs. This is similar to the 'valid' option in the conv2 function.
whos filteredImage*Name Size Bytes Class Attributes filteredImage1 264x264 557568 double filteredImage2 260x260 540800 double filteredImage3 256x256 524288 double
Because the image was padded to accommodate the largest box filter prior to computing the integral image, no image content is lost. filteredImage1 and filteredImage2 have additional padding that can be cropped.
extraPadding1 = (maxFilterSize - filterSizes(1,:))/2; filteredImage1 = filteredImage1(1+extraPadding1(1):end-extraPadding1(1),... 1+extraPadding1(2):end-extraPadding1(2) ); extraPadding2 = (maxFilterSize - filterSizes(2,:))/2; filteredImage2 = filteredImage2(1+extraPadding2(1):end-extraPadding2(1),... 1+extraPadding2(2):end-extraPadding2(2) ); figure imshow(filteredImage1,[]) title('Image filtered with [7 7] box filter')
![Figure contains an axes object. The hidden axes object with title Image filtered with [7 7] box filter contains an object of type image.](../examples/images/win64/ApplyMultipleFiltersToIntegralImageExample_03.png)
figure
imshow(filteredImage2,[])
title('Image filtered with [11 11] box filter')![Figure contains an axes object. The hidden axes object with title Image filtered with [11 11] box filter contains an object of type image.](../examples/images/win64/ApplyMultipleFiltersToIntegralImageExample_04.png)
figure
imshow(filteredImage3,[])
title('Image filtered with [15 15] box filter')![Figure contains an axes object. The hidden axes object with title Image filtered with [15 15] box filter contains an object of type image.](../examples/images/win64/ApplyMultipleFiltersToIntegralImageExample_05.png)
See Also
integralImage | integralBoxFilter | integralBoxFilter3 | integralImage3