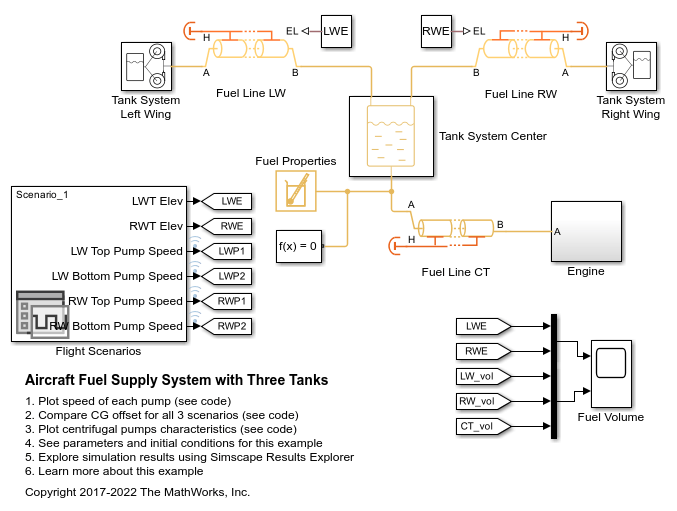
Centrifugal Pump (TL)
Centrifugal pump in a thermal liquid network
Libraries:
Simscape /
Fluids /
Thermal Liquid /
Pumps & Motors
Description
The Centrifugal Pump (TL) block represents a centrifugal pump that transfers energy from the shaft to a fluid in a thermal liquid network. The pressure differential and mechanical torque are functions of the pump head and brake power, which depend on the pump capacity. You can parameterize the pump analytically or by linear interpolation of the tabulated data. The pump affinity laws define the core physics of the block, which scales the pump performance by the ratio of the current to the reference values of the pump angular velocity and impeller diameter.
By default, the flow and pressure gain are from port A to port B. Port C represents the pump casing, and port R represents the pump shaft. You can specify the normal operating shaft direction in the Mechanical orientation parameter. If the shaft begins to spin in the opposite direction, the pressure difference across the pump drops to zero.
Analytical Parameterization
When you set Pump parameterization to
Capacity, head, and brake power at reference shaft
speed, the block calculates the pressure gain over the pump as a
function of the pump affinity laws and the reference pressure differential
where:
ΔHref is the reference pump head, which the block derives from a quadratic fit of the pump pressure differential between the values of the Maximum head at zero capacity, Nominal head, and Maximum capacity at zero head parameters.
ω is the shaft angular velocity, where ω = ωR – ωC.
ωref is the value of the Reference shaft speed parameter.
is the value of the Impeller diameter scale factor parameter. The block does not reflect changes in pump efficiency due to pump size.
ρ is the network fluid density.
The shaft torque is
The block calculates the reference brake power, Wbrake,ref, as capacity·head/efficiency. The pump efficiency curve is quadratic and its peak corresponds to the Nominal brake power parameter. The pump efficiency curve falls to zero when capacity is zero or maximum.
The block calculates the reference capacity as
The block returns a warning when the block flow rate becomes negative or exceeds
the maximum pump capacity if the Check if operating beyond normal pump
operation parameter is Warning.
1-D Tabulated Data Parameterization
When you set Pump parameterization to 1D
tabulated data - head and brake power vs. capacity at reference shaft
speed, the pressure gain over the pump is a function of the
Reference head vector parameter,
ΔHref, which is a function of the
reference capacity, qref
where g is the gravitational acceleration.
The block bases the shaft torque on the Reference brake power vector parameter, Wref, which is a function of the reference capacity
where ρref is the value of the Reference density parameter. The reference capacity is
which the block uses to interpolate the values of the Reference capacity vector, Reference head vector, and Reference brake power vector parameters as a function of qref.
When the simulation is outside the range of the provided tables, the block extrapolates the head based on the average slope of the pump curves and brake power to the nearest point.
2-D Tabulated Data Parameterization
When you set Pump parameterization to 2D
tabulated data - head and brake power vs. capacity and shaft
speed, the pressure gain over the pump is a function of the
Head table, H(q,w) parameter,
ΔHref, which is a function of the
reference capacity, qref, and the shaft
speed, ω
The shaft torque is a function of the Brake power table, Wb(q,w) parameter, Wref, which is a function of the reference capacity, qref, and the shaft speed, ω
The reference capacity is
When the simulation is outside the range of the provided tables, the block extrapolates the head based on the average slope of the pump curves and brake power to the nearest point.
If your table has unknown data points, use NaN in the
Head table, H(q,w) and Brake power table,
Wb(q,w) parameters in place of these values. The block fills in
the NaN elements by extrapolating based on the average slope
of the pump curves. Do not use artificial numerical values because these values
distort pump behavior when operating in that region. When using unknown data:
The
NaNelements in the table must be contiguous.The positions of the
NaNelements in the Head table, H(q,w) and Brake power table, Wb(q,w) parameters must match.The
NaNelements must be located in the lower-left portion of the table, which corresponds to the highest capacity and lowest shaft speed.
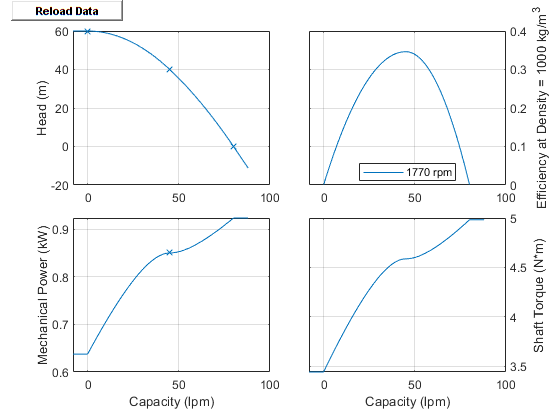
Visualizing the Pump Curve
You can check the parameterized pump performance by plotting the head, power, efficiency, and torque as a function of the flow. To generate a plot of the current pump settings, right-click the block and select Fluids > Plot Pump Characteristics. If you change the settings or data, click Apply on the block parameters and click Reload Data on the pump curve figure.
The default block parameterization creates these plots:
Energy Balance
Mechanical work is a result of the energy exchange from the shaft to the fluid. The governing energy balance equation is
where:
ΦA is the energy flow rate at port A.
ΦB is the energy flow rate at port B.
The pump hydraulic power is a function of the pressure difference between pump ports
Assumptions and Limitations
If the shaft rotates opposite to the setting of the Mechanical orientation parameter, the pressure difference across the block drops to zero and the results may not be accurate.
The block does not account for dynamic pressure in the pump. The block only considers pump head due to static pressure.