1xEV-DO Waveform Generation
This example shows how to generate standard-compliant forward (downlink) and reverse (uplink) 1xEV-DO waveforms using the Communications Toolbox™.
Introduction
The Communications Toolbox can be used to generate preset or customized standard-compliant forward and reverse, Release 0 and Revision A 1xEV-DO waveforms.
The generated waveforms can be used for the following applications:
Golden reference for transmitter implementations
Receiver testing and algorithm development
Testing RF hardware and software
Interference testing
Waveform Generation Techniques
Waveforms can be generated using the
evdoForwardWaveformGeneratorandevdoReverseWaveformGeneratorfunctions. The input of these functions is a structure containing top-level waveform parameters as well as substructures containing channel- or packet-specific parameters. This example will illustrate how such structures can be constructed from scratch.Preset structure configurations can be created using the
evdoForwardReferenceChannelsandevdoReverseReferenceChannelsfunctions. Such preset configurations can represent common Test and Measurement scenarios or provide a good starting point (wizard) for customizing a waveform configuration.
Generation of Preset-driven Forward and Reverse 1xEV-DO Waveforms
The preset structure configurations can then be passed to the waveform generation functions. For example, the following commands generate Revision A and Release 0 forward and reverse waveforms, respectively.
numPackets = 10; forwardPresetConfig = evdoForwardReferenceChannels('RevA-5120-2-64',numPackets); forwardPresetWaveform = evdoForwardWaveformGenerator(forwardPresetConfig); reversePresetConfig = evdoReverseReferenceChannels('Rel0-38400',numPackets); reversePresetWaveform = evdoReverseWaveformGenerator(reversePresetConfig);
Generation of a Forward 1xEV-DO Waveform Using Full Parameter List
Next, we illustrate the creation of equivalent configuration structures from scratch. This is also useful for customizing the preset configurations.
% Create top-level waveform parameters: fManualConfig.Release = 'RevisionA'; % 'Release0' or 'RevisionA' fManualConfig.PNOffset = 0; % PN Offset of the Base station fManualConfig.IdleSlotsWithControl = 'Off'; fManualConfig.EnableControl = 'On'; fManualConfig.OversamplingRatio = 4; % Upsampling factor fManualConfig.FilterType = 'cdma2000Long'; % Filter coefficients:'cdma2000Long','cdma2000Short','Custom','Off' fManualConfig.InvertQ = 'Off'; % Negate the imaginary output fManualConfig.EnableModulation = 'Off'; % Enable modulation fManualConfig.ModulationFrequency = 0; % Modulation frequency (Hz) fManualConfig.NumChips = 41600; % Number of chips in the waveform % Create a input message source for the packets: pds.MACIndex = 0; % MAC index associated with data pds.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector pds.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fManualConfig.PacketDataSources = pds; % Add the data source specification to the waveform configuration % Create a single packet: fPacket.MACIndex = 0; % MAC index associated with this packet fPacket.PacketSize = 5120; % Packet size options: 128,256,512,1024,2048,4096,5120 bits fPacket.NumSlots = 2; % Number of slots options: 1,2,4,8,16 fPacket.PreambleLength = 64; % Preamble length options: 64,128,256,512,1024 chips fManualConfig.PacketSequence = repmat(fPacket,1,numPackets); % Generate waveform: forwardManualWaveform = evdoForwardWaveformGenerator(fManualConfig); % Demonstrate that the above two parameterization approaches are equivalent: if(isequal(forwardPresetConfig, fManualConfig)) disp(['Configuration structures generated with and without the ' ... 'evdoForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Configuration structures generated with and without the evdoForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.
Generation of a Reverse 1xEV-DO Waveform Using Full Parameter List
% Create top-level waveform parameters: rManualConfig.Release = 'Release0'; % 'Release0' or 'RevisionA' rManualConfig.LongCodeMaskI = 0; % Initial long code mask for I channel rManualConfig.LongCodeMaskQ = 0; % Initial long code mask for Q channel rManualConfig.OversamplingRatio = 4; % Upsampling factor rManualConfig.FilterType = 'cdma2000Long'; % Filter coefficients:'cdma2000Long','cdma2000Short','Custom','Off' rManualConfig.InvertQ = 'Off'; % Negate the imaginary output rManualConfig.EnableModulation = 'Off'; % Enable modulation rManualConfig.ModulationFrequency = 0; % Modulation frequency (Hz) rManualConfig.NumChips = 327680; % Number of chips in the waveform % Create a single packet: rPacket.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) rPacket.DataSource = {'PN9',1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector rPacket.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding rPacket.DataRate = 38400; % Data rate (bps) rManualConfig.PacketSequence = repmat(rPacket,1,numPackets); % Add a Pilot Channel: pich.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the pilot channel pich.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) pich.DataSource = {'PN9',1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector pich.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding rManualConfig.PilotChannel = pich; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration % Add an ACK Channel, but do not enable it: ach.Enable = 'Off'; % Do not enable the ack channel ach.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) ach.DataSource = {'PN9',1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector rManualConfig.ACKChannel = ach; % Add the disabled channel specification to the waveform configuration % Generate waveform: reverseManualWaveform = evdoReverseWaveformGenerator(rManualConfig); % Demonstrate that the above two parameterization approaches are equivalent: if(isequal(reversePresetConfig,rManualConfig)) disp(['Configuration structures generated with and without the ' ... 'evdoForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Configuration structures generated with and without the evdoForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.
Waveform Comparison
Compare the waveforms generated using both approaches described above and see that the generated waveforms are identical.
if(isequal(forwardPresetWaveform,forwardManualWaveform)) disp(['Forward waveforms generated with and without the ' ... 'evdoForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Forward waveforms generated with and without the evdoForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.
if(isequal(reversePresetWaveform,reverseManualWaveform)) disp(['Reverse waveforms generated with and without the ' ... 'evdoReverseReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Reverse waveforms generated with and without the evdoReverseReferenceChannels function are the same.
Customizing Configurations
The configuration structures can be customized in order to create a waveform that better suits your objective. For example:
rManualConfig2 = rManualConfig; rPacket.Power = -10; % Relative channel power (dBW) rPacket.DataSource = {'PN23',1}; % Input message: {'PNX',Seed} or numerical vector rPacket.EnableCoding = 'Off'; % Enable channel coding rPacket.DataRate = 38400; % Data rate (bps) rManualConfig2.PacketSequence = repmat(rPacket,1,numPackets); % Regenerate the waveform accounting for the customizations: reverseManualWaveform2 = evdoReverseWaveformGenerator(rManualConfig2);
Plot Spectrum of Generated 1xEV-DO Waveforms
chiprate = 1.2288e6; % Chip rate of the baseband waveform (SR1) spectrumPlot = spectrumAnalyzer( ... SampleRate=chiprate*fManualConfig.OversamplingRatio, ... Title='Spectrum of Forward 1xEV-DO Waveform', ... YLimits=[-180,40]); spectrumPlot(forwardManualWaveform);
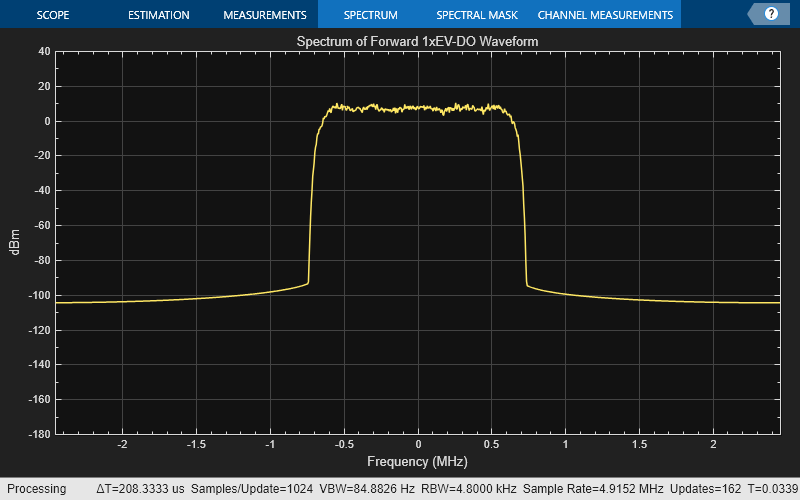
spectrumPlot2 = spectrumAnalyzer( ... SampleRate=chiprate*rManualConfig.OversamplingRatio, ... Title='Spectrum of Reverse 1xEV-DO Waveform', ... YLimits = [-180,40]); spectrumPlot2(reverseManualWaveform2);
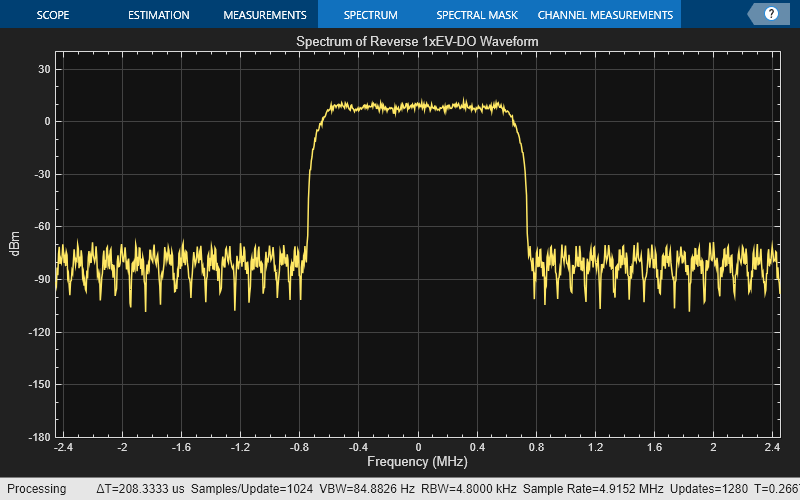
Selected Bibliography
C.S0024-A v3.0: cdma2000 High Rate Packet Data Air Interface Specification.