optimize
Syntax
Description
optimizedelement = optimize(element,frequency,objectivefunction,propertynames,bounds)
optimizedelement = optimize(___,Name=Value)
Examples
Maximize Gain of Dipole Antenna
Create and view a default dipole antenna.
ant = dipole; show(ant)

Maximize the gain of the antenna by changing the antenna length from 3 m to 7 m and the width from 0.11 m to 0.13 m.
Optimize the antenna at a frequency of 75 MHz.
optAnt = optimize(ant,75e6,"maximizeGain", ... {'Length','Width'}, {3 0.11; 7 0.13})
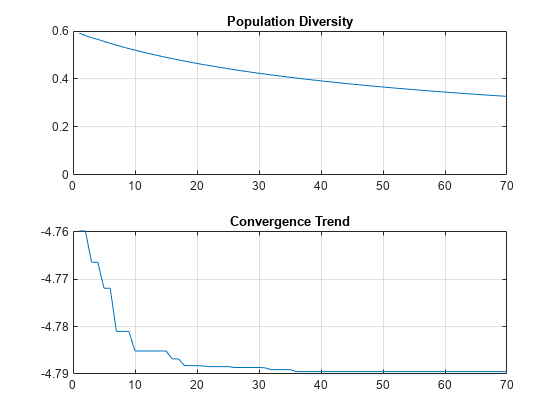
optAnt =
dipole with properties:
Length: 4.7973
Width: 0.1100
FeedOffset: 0
Conductor: [1x1 metal]
Tilt: 0
TiltAxis: [1 0 0]
Load: [1x1 lumpedElement]
show(optAnt)

Optimize E-Notch Microstrip Patch Antenna for Gain with Geometric Constraints
This example shows how to optimize an E-Notch microstrip patch antenna for gain with constraints on its geometry.
Create E-Notch Microstrip Patch Antenna
Create an E-Notch microstrip patch antenna operating at 2GHz and vary its center arm notch length and width.
% Create E-notch microstrip antenna
ant = design(patchMicrostripEnotch,2e9);
ant.CenterArmNotchLength = 0.0073;
ant.CenterArmNotchWidth = 0.0144;Plot its radiation pattern and check the maximum gain value.
% Check the gain figure pattern(ant,2e9,Type="gain")

Optimize E-Notch Microstrip Patch Antenna for Gain
Define the design variables, and their lower and upper bounds.
designVariables = {'CenterArmNotchLength','NotchLength','Width','CenterArmNotchWidth','NotchWidth'};
XVmin = [0.001, 0.03, 0.03, 0.01, 0.001];
XVmax = [0.02, 0.06, 0.07, 0.03, 0.009];Add geometric constraints
Prepare coefficients in the form of a matrix with reference to below linear inequalities:
Rewrite the inequalities 1 & 2 in the form of
Convert these inequalities to a matrix of form , where is coefficient matrix and is constant matrix. Write the coefficients as per the order of design variables.
A = [5,-1,0,0,0;...
0,0,-1,1,2];
b = [0;0];Define a structure to contain both the coefficient and constant matrices.
constraintsStructure.A = A; constraintsStructure.b = b;
Optimize E-Notch microstrip patch antenna and check its gain
Run the optimization on E-Notch microstrip patch antenna leveraging these constraints. Visualize the optimized design and plot the radiation pattern.
optAnt = optimize(ant, 2e9, "maximizeGain", designVariables, {XVmin;XVmax}, Iterations=50, GeometricConstraints=constraintsStructure);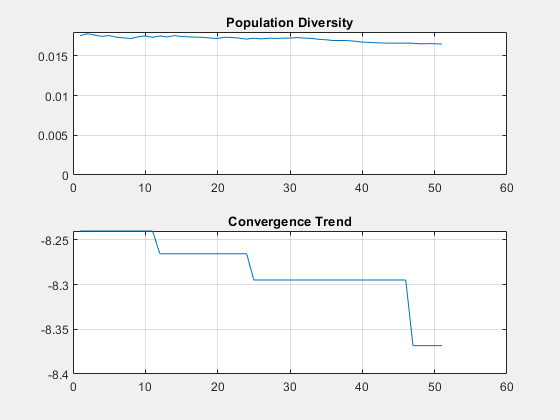
figure show(optAnt)

figure
pattern(optAnt,2e9,Type="gain")
Input Arguments
element — Antenna or array to optimize
antenna object | array object | customAntenna object
Antenna or array, specified as an antenna object from the Antenna Catalog, array object from the Array Catalog, or
customAntenna object.
Note
To optimize pcbStack antenna, use PCB Antenna
Designer app.
Example: dipole
Example: linearArray(Element=dipole)
Example: customAntenna(Shape=shape.Rectangle)
frequency — Frequency to optimize antenna or array
positive scalar
Operating frequency of the antenna or array to optimize, specified as a positive scalar in Hertz.
Example: 70e6
Data Types: double
objectivefunction — Objective of antenna or array optimization
"maximizeGain" | "fronttoBackLobeRatio" | "maximizeBandwidth" | "minimizeBandwidth" | "maximizeSLL" | "minimizeArea" | custom objective function
Objective of antenna or array optimization, specified as a string from one of the following:
maximizeGain— Maximize the gain of the given antenna or array elementfronttoBackRatio— Increase the front-lobe-to-back-lobe ratio of the antenna or array elementmaximizeBandwidth— Maximize the operation bandwidth of the antenna or array element. Use this objective function for optimizing antennas or arrays for wideband applications.minimizeBandwidth— Minimize the operation bandwidth of the antenna or array element. Use this objective function for optimizing antennas or arrays for narrowband applications.maximizeSLL— Maximize the ratio between the front lobe and the first side lobes of the antenna or array pattern.minimizeArea— Minimizes the maximum area occupied by the antenna or the array element. If the dimension of the element in the array is smaller than the aperture, the objective function minimizes the array aperture.Custom objective function — Optimizes the antenna or array as per the user defined objective function.
Data Types: string
propertynames — Properties of antenna or array
cell array of character vectors
Properties of the antenna or array object to optimize, specified as a cell array of character vectors. The property names are selected as the design variables in optimization.
Example: {'Length','Width'}
Data Types: cell
bounds — Lower and upper bounds of design variables
two-row cell array
Lower and upper bounds of design variables, specified as a two-row cell array.
Example: {3 0.11; 7 0.13}
Data Types: double
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: Constraints={'Area<0.03'}
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: 'Constraints',{'Area<0.03'}
Constraints — Optimization constraints
cell array of strings or character vectors
Antenna or array optimization constraints, specified as a cell array of strings or character vectors. Each character vector or string must be of the form: (analysis function) (inequality sign) (value). You can specify any of the following analysis functions:
Areain meter squareVolumein meter cubeS11in dBGainin dBiF/Bin dBiSLLin dBi
The inequality signs '<' or '>' and the
values specifies the analysis function limits. For example, 'Area <
0.03' indicates that the area of the optimizing antenna must be less than
0.03 square meter.
Example: {'Area<0.03'}
Data Types: char | string
Weights — Weight or penalty of each constraint function
vector of positive integers in the range (1,100)
Weight or penalty of each constraint function, specified as a vector of positive integers in the range (1,100). If the penalty is set to high, a higher priority is given to the constraint function in case of multiple constraint optimization. All constraint functions are weighted equally by default.
Example: 8
Data Types: double
FrequencyRange — Range of frequencies for vector frequency analysis
vector of positive numbers
Range of frequencies for vector frequency analysis like S-parameters, specified as a vector of positive numbers with each element unit in Hertz.
The default frequency range is obtained from the center frequency considering a bandwidth of less than 10 percent.
Example: linspace(1e9,2e9,10)
Data Types: double
ReferenceImpedance — Reference impedance of optimizing antenna or array
50 (default) | scalar
Reference impedance of antenna or array being optimized, specified as a scalar in ohms.
Example: 75
Data Types: double
MainLobeDirection — Azimuth and elevation of main lobe
[0,90] (default) | two-element vector
Azimuth and elevation of main lobe of antenna or array being optimized, specified as a two-element vector with each element unit in degrees. The first element represents azimuth and the second element represents elevation.
Example: [20 30]
Data Types: double
Iterations — Number of iterations to run optimizer
200 (default) | positive scalar
Number of iterations to run the optimizer after you build the model, specified as a positive scalar.
Example: 40
Data Types: double
UseParallel — Use Parallel Computing Toolbox™ during optimization
false (default) | true
Use Parallel Computing Toolbox during optimization, specified as either true or
false. Use the canUseGPU
function to check if dedicated GPU is available for computations and Parallel Computing Toolbox is installed and ready for use.
Example: true
Data Types: logical
EnableCoupling — Enable mutual coupling of elements in arrays during optimization
true (default) | false
Enable mutual coupling of elements in an array during optimization, specified as
either true or false.
Example: false
Data Types: logical
EnableLog — Enable printing iteration number and value of convergence on command line
false (default) | true
Enable printing iteration number and value of convergence on the command line,
specified as either true or false.
Example: true
Data Types: logical
GeometricConstraints — Geometric constraints
structure
Geometric constraints for optimization, specified as a structure of coefficient matrix and constant vector.
Specify linear inequality constraints in the A matrix and b vector.
A is a real M-by-N matrix where M is the number of inequalities, and N is the number of design variables. A holds the design variable coefficients of the inequalities.
b is a real M-element column vector and holds the constants of inequalities corresponding to the coefficients in A.
For example, consider an optimization problem consisting of 5 design variables as follows:
designVariables = {'CenterArmNotchLength','NotchLength','Width',...
'CenterArmNotchWidth','NotchWidth'};5*CenterArmNotchLength - NotchLength < 0
CenterArmNotchWidth + 2*Notchwidth - Width < 0
Define the A and b as follows:
A = [5,-1,0,0,0;...
0,0,-1,1,2];
b = [0;0];Example: A=[5,-1,0,0,0; 0,0,-1,1,2]; b=[0;0]; structure.A=A;
structure.b=b;
Data Types: struct
Output Arguments
optimizedelement — Optimized antenna or array element
antenna object | array object | customAntenna object
Optimized antenna or array element, returned as an antenna, array, or
customAntenna object.
Version History
Introduced in R2020bR2024a: Use custom objective function and geometric constraints for optimization
Specify a custom objective function to define antenna or array optimization objectives.
Use custom geometric constraints defined by linear inequalities of design variables for antenna or array optimization. Specify custom geometric constraints in the new
GeometricConstraintsname-value argument.
See Also
canUseGPU | fmincon (Optimization Toolbox)
Topics
- SADEA Optimization of Six-Element Yagi-Uda Antenna using Custom Objective Function
- Direct Search Based Optimization of Six-Element Yagi-Uda Antenna
- Surrogate Based Optimization Design of Six-Element Yagi-Uda Antenna
- Optimization of Antenna Array Elements Using Antenna Array Designer App
- Maximizing Gain and Improving Impedance Bandwidth of E-Patch Antenna
- Antenna Optimization Algorithm
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)